|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
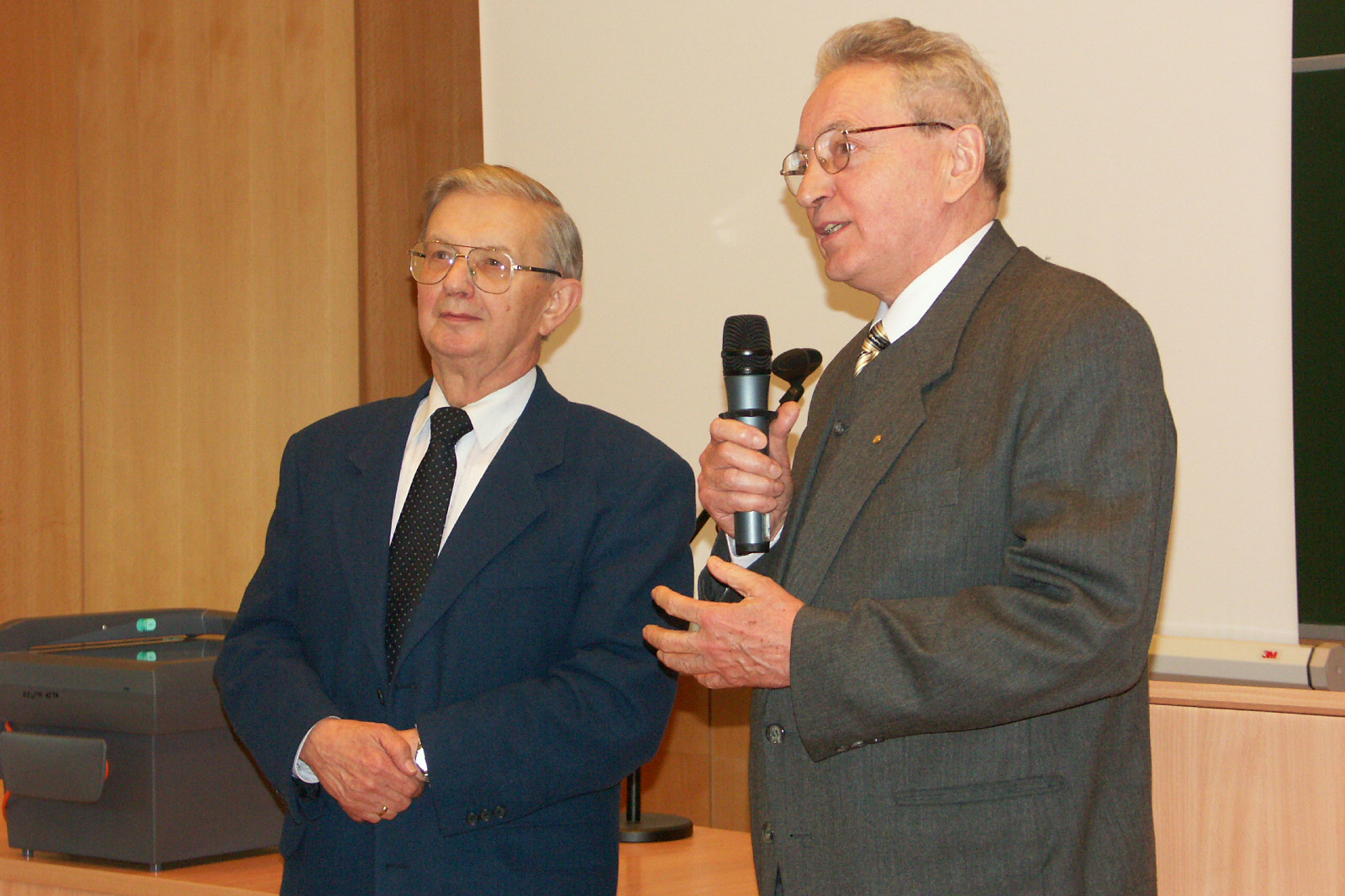
Prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
| 1994-10 <> 2022-03
|
|
|
Kierownik Zakładu Fizyki Makromolekularnej w latach 1994-2016
Dyrektor Centrum Nanobiomedycznego UAM w latach 2010-2022
|
|
|
 0000-0002-1665-6077 0000-0002-1665-6077
 2132982 / E-8862-2017 2132982 / E-8862-2017
 7004205616 7004205616
|
|
|
Zainteresowania naukowe: | Główne zainteresowania badawcze prof. S. Jurgi koncentrują się na strukturze i dynamice materii miękkiej analizowanej za pomocą obrazowania NMR, metod rozproszeniowych (SAXS, WAXS), mikroskopii elektronowej, sił atomowych oraz optycznej, relaksacji oraz dyfuzji NMR, technik modelowania komputerowego, spektroskopi dielektrycznej i FTIR. Profesor Jurga jest autorem i współautorem 190 publikacji naukowych w renomowanych czasopismach o zasięgu krajowym i międzynarodowym. Uczestniczył w wielu międzynarodowych projektach badawczych, był promotorem 20 doktorantów.
Ma bogate doświadczenie we współpracy międzynarodowej, był m.in. profesorem wizytującym w Cornell University, Uniwersytecie Stanowym Północnej Karoliny w USA, w Uniwersytecie Południowej Afryki w Pretorii w RPA, w Centrum Badań Atomowych w Saclay pod Paryżem. Prof. Jurga był laureatem Fundacji Maxa Plancka jako stypendysta w Instytucie Maxa Plancka do badań polimerowych w Moguncji, Niemcy, pracował na Uniwersytecie Illinois w Urbana Champaign, USA, w Instytucie Jozefa Stefana w Słowenii, i w innych instytucjach.
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Publikacje
Projekty
Doktorzy
Magistrowie
Licencjusze
Seminaria
|
317. |
Maciejewska B.M., Wychowaniec J.K., Woźniak-Budych M., Popenda Ł., Warowicka A., Golba K., Litowczenko J., Fojud Z., Wereszczyńska B., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 20(1), 979-991 (2019) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1080/14686996.2019.1667737 (Pobrane: 2020-06-04) |
|
|
|
316. |
Rębiś T., Falkowski M., Kryjewski M., Popenda Ł., Sobotta Ł., Jurga S., Marszall M.P., Mielcarek J., Milczarek G., Goślinski T. |
|
|
|
|
|
Dyes and Pigments, 171, 107660 (2019) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2019.107660 (Pobrane: 2020-12-30) |
|
|
|
315. |
Grześkowiak B.F., Tuśnio K., Woźniak A., Szalata M., Lipiński D., Jurga S., Słomski R. |
|
|
|
|
|
Biosensors-Basel, 9(4), 116 (2019) |
|
|
DOI: 10.3390/bios9040116 (Pobrane: 2020-12-30) |
|
|
|
314. |
Kertmen A., Przysiecka Ł., Coy E., Popenda Ł., Andruszkiewicz R., Jurga S., Milewski S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Langmuir, 35(44), 14397-14397 (2019) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b03088 (Pobrane: 2020-12-30) |
|
|
|
313. |
Warowicka A., Popenda Ł., Bartkowiak G., Musidlak O., Litowczenko-Cybulska J., Kuźma D., Nawrot R., Jurga S., Goździcka-Józefiak A. |
|
|
|
|
|
Phytomedicine, 64, 152919 (2019) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.152919 (Pobrane: 2020-12-30) |
|
|
|
312. |
Litowczenko J., Maciejewska B.M., Wychowaniec J.K., Kościnski M., Jurga S., Warowicka A. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research part A, 107(10), 2244-2256 (2019) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1002/jbm.a.36733 (Pobrane: 2020-12-30) |
|
|
|
311. |
Szutkowski K., Sikorska E., Bakanovych I., Choudhury A.R., Perdih A., Jurga S., Novic M., Zhukov I. |
|
|
|
|
|
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(17), 4172 (2019) |
|
|
DOI: 10.3390/ijms20174172 (Pobrane: 2020-12-30) |
|
|
|
310. |
Matuła K., Richter Ł., Janczuk-Richter M., Nogala W., Grzeszkowiak M., Peplińska B., Jurga S., Wyroba E., Suski S., Bilski H., Silesian A., Bluyssen H.A.R., Derebecka N., Wesoły J., Łoś J.M., Łoś M., Decewicz P., Dziewit Ł., Paczesny J., Hołyst R. |
|
|
|
|
|
Scientific Reports, 9, 8575 (2019) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-44727-w (Pobrane: 2020-12-30) |
|
|
|
309. |
Grabowska M., Wawrzyniak D., Rolle K., Chomczyński P., Oziewicz S., Jurga S., Barciszewski J. |
|
|
|
|
|
Food & Function, 10(6), 3090-3102 (2019) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1039/c9fo00580c (Pobrane: 2020-12-30) |
|
|
|
308. |
Grabowska M., Wawrzyniak D., Rolle K., Chomczyński P., Oziewicz S., Jurga S., Barciszewski J. |
|
|
|
|
|
Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 388(1), 248-267 (2019) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2019.03.003 (Pobrane: 2020-12-30) |
|
|
|
307. |
Wiesner M., Roberts R.H., Lin J.F., Akinwande D., Hesjedal T., Duffy L.B., Wang S.M., Song Y.X., Jenczyk J., Jurga S., Mróz B. |
|
|
|
|
|
Scientific Reports, 9, 6147 (2019) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-42598-9 (Pobrane: 2020-12-30) |
|
|
|
306. |
Kertmen A., Przysiecka Ł., Coy E., Popenda Ł., Andruszkiewicz R., Jurga S., Milewski S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Langmuir, 35(15), 5281-5293 (2019) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b04250 (Pobrane: 2020-12-30) |
|
|
|
305. |
Kristinaityte K., Zalewski T., Kempka M., Sakirzanovas S., Baziulyte-Paulaviciene D., Jurga S., Rotomskis R., Valeviciene N.R. |
|
|
|
|
|
Applied Magnetic Resonance, 50(4) SI, 553-561 (2019) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1007/s00723-018-1105-z (Pobrane: 2020-12-28) |
|
|
|
304. |
Jenczyk J., Woźniak-Budych M., Jancelewicz M., Jarek M., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Polymer, 167, 130-137 (2019) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2019.01.080 (Pobrane: 2019-03-19) |
|
|
|
303. |
Grabowska M., Grześkowiak B.F., Szutkowski K., Wawrzyniak D., Głodowicz P., Barciszewski J., Jurga S., Rolle K., Mrówczyński R. |
|
|
|
|
|
PloS ONE, 14(3), e0213852 (2019) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0213852 (Pobrane: 2020-12-28) |
|
|
|
302. |
Kertmen A., Barbe E., Szkoda M., Siuzdak K., Babacic V., Torruella P., Iatsunskyi I., Kotkowiak M., Rytel K., Estrade S., Peiro F., Jurga S., Li Yanguang, Coy E. |
|
|
|
|
|
Advanced Materials Interfaces, 6(3), 1801286 (2019) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1002/admi.201801286 (Pobrane: 2020-12-28) |
|
|
|
301. |
Mrówczyński R., d'Ischia M., Lee H., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Biomimetics, 4(1), 14 (2019) |
|
|
DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics4010014 (Pobrane: 2020-12-27) |
|
|
|
300. |
Maziukiewicz D., Grześkowiak B.F., Coy E., Jurga S., Mrówczyński R. |
|
|
|
|
|
Biomimetics, 4(1), 3 (2019) |
|
|
DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics4010003 (Pobrane: 2021-01-27) |
|
|
|
299. |
Jurga S., Barciszewski J. |
|
|
|
|
|
Systems Biology: Book Series: RNA Technologies, Ed. by Jurga S., Barciszewsk J., , V-VII (2019) |
|
|
ISBN: 978-3-030-14791-4 (Pobrane: 2020-12-26) |
|
|
|
298. |
Pshyk A.V., Coy E., Kempiński M., Scheibe B., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Materials Research Letters, 7(6), 244-250 (2019) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1080/21663831.2019.1594428 (Pobrane: 2020-12-28) |
|
|
|
297. |
Wieczorek E., Piskorz J., Popenda Ł., Jurga S., Mielcarek J., Goślinski T. |
|
|
|
|
|
Heterocyclic Communications, 25(1), 1-7 (2019) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1515/hc-2019-0001 (Pobrane: 2020-12-28) |
|
|
|
296. |
Jędrzak A., Grześkowiak B.F., Coy E., Wojnarowicz J., Szutkowski K., Jurga S., Jesionowski T., Mrówczyński R. |
|
|
|
|
|
Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 173, 698-708 (2019) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.10.045 (Pobrane: 2019-03-21) |
|
|
|
295. |
Mrówczyński R., d'Ischia M., Lee H., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Biomimetics, 3(4), 37 (2018) |
|
|
DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics3040037 (Pobrane: 2020-12-27) |
|
|
|
294. |
Flak D., Przysiecka Ł., Nowaczyk G., Scheibe B., Kościnski M., Jesionowski T., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 20(11), 306 (2018) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1007/s11051-018-4416-y (Pobrane: 2020-12-27) |
|
|
|
293. |
Paprzycka M., Scheibe B., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Fibres & Textiles in Eastern Europe, 26(6), 51-56 (2018) |
|
|
DOI: 10.5604/01.3001.0012.5170 (Pobrane: 2020-12-27) |
|
|
|
292. |
Kravchenko Y.O., Coy L.E., Peplińska B., Iatsunskyi I., Zaleski K., Kempiński M., Beresnev V.M., Konarski P., Jurga S., Pogrebnjak A.D. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 767, 483-495 (2018) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.07.090 (Pobrane: 2020-12-27) |
|
|
|
291. |
Bagdasaryan A.A., Pshyk A.V., Coy L.E., Kempiński M., Pogrebnjak A.D., Beresnev V.M., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Materials Letters, 229, 364-367 (2018) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2018.07.048 (Pobrane: 2020-12-27) |
|
|
|
290. |
Tillo A., Kryjewski M., Bendzińska-Berus W., Langer D., Rębiś T., Popenda Ł., Jurga S., Mielcarek J., Goślinski T., Tykarska E. |
|
|
|
|
|
Synthetic Metals, 244, 66-72 (2018) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.synthmet.2018.07.002 (Pobrane: 2020-12-27) |
|
|
|
289. |
Graniel O., Fedorenko V., Viter R., Iatsunskyi I., Nowaczyk G., Weber M., Zaleski K., Jurga S., Smyntyna V., Miele P, Ramanavicius A., Balme S., Bechelany M. |
|
|
|
|
|
Materials Science and Engineering B - Advanced Functional Solid-State Materials, 236, 139-146 (2018) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.mseb.2018.11.007 (Pobrane: 2020-12-27) |
|
|
|
288. |
Lewandowski M., Pabisiak T., Michalak N., Miłosz Z., Babacic V., Wang Y., Hermanowicz M., Palotas K., Jurga S., Kiejna A. |
|
|
|
|
|
Nanomaterials, 8(10, 828 (2018) |
|
|
DOI: 10.3390/nano8100828 (Pobrane: 2020-12-27) |
|
|
|
287. |
Pshyk A.V., Kravchenko Y., Coy E., Kempiński M., Iatsunskyi I., Zaleski K., Pogrebnjak A.D., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Surface & Coatings Technology, 350, 376-390 (2018) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.07.010 (Pobrane: 2020-12-27) |
|
|
|
286. |
Ivashchenko O., Przysiecka Ł., Peplińska B., Jarek M., Coy E., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Scientific Reports, 8, 13260 (2018) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-31686-x (Pobrane: 2020-12-27) |
|
|
|
285. |
Pogrebnjak A.D., Beresnev V.M., Bondar O.V., Postolnyi B.O., Zaleski K., Coy E., Jurga S., Lisovenko M.O., Konarski P., Rebouta L., Araujo J.P. |
|
|
|
|
|
Materials & Design, 153, 47-59 (2018) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2018.05.001 (Pobrane: 2020-12-27) |
|
|
|
284. |
Istsunskyi I., Baitimirova M., Coy E., Yate L., Viter R., Ramanavicius A., Jurga S., Bechelany M., Erts D. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 34(9), 1487-1493 (2018) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.jmst.2018.03.022 (Pobrane: 2020-12-26) |
|
|
|
283. |
Bagdasaryan A.A., Pshyk A.V., Coy L.E., Konarski P., Misnik M, Ivashchenko V.I., Kempiński M., Mediukh N.R., Pogrebnjak A.D., Beresnev V.M., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Composites: part B - Engineering, 146, 132-144 (2018) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.04.015 (Pobrane: 2020-12-26) |
|
|
|
282. |
Pogrebnjak A.D., Ivashchenko V.I., Skrynskyy P.L., Bondar O.V., Konarski P., Zaleski K., Jurga S., Coy E. |
|
|
|
|
|
Composites: part B - Engineering, 142, 85-94 (2018) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.01.004 (Pobrane: 2020-12-26) |
|
|
|
281. |
Siwińska-Stefańska K., Kubiak A., Piasecki A., Gościanska J., Nowaczyk G., Jurga S., Jesionowski T. |
|
|
|
|
|
Materials, 11(5), 841 (2018) |
|
|
DOI: 10.3390/ma11050841 (Pobrane: 2020-12-26) |
|
|
|
280. |
Wieczorek E., Młynarczyk D.T., Kucińska M., Długaszewska J., Piskorz J., Popenda Ł., Szczółko W., Jurga S., Murias M., Mielcarek J., Goślinski T. |
|
|
|
|
|
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 150, 64-73 (2018) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.02.064 (Pobrane: 2020-12-26) |
|
|
|
279. |
Ivashchenko O., Peplińska B., Gapiński J., Flak D., Jarek M., Załęski K., Nowaczyk G., Pietralik Z., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Scientific Reports, 8, 4041 (2018) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-22426-2 (Pobrane: 2018-03-20) |
|
|
|
278. |
Skupin-Mrugalska P., Sobotta Ł., Warowicka A., Wereszczyńska B., Zalewski T., Gierlich P., Jarek M., Nowaczyk G., Kempka M., Gapiński J., Jurga S., Mielcarek J. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, 180, 1-14 (2018) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2017.11.025 (Pobrane: 2018-03-20) |
|
|
|
277. |
Mrówczyński R., Jędrzak A., Szutkowski K., Grześkowiak B., Coy E., Markiewicz R., Jesionowski T., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Nanomaterials, 8(3), Article Number: UNSP 170 (2018) |
|
|
DOI: 10.3390/nano8030170 (Pobrane: 2020-10-23) |
|
|
|
276. |
Scheibe B., Mrówczyński R., Michalak N., Zaleski K., Matczak M., Kempiński M., Pietralik Z., Lewandowski M., Jurga S., Stobiecki F. |
|
|
|
|
|
Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology, 9, 591-601 (2018) |
|
|
DOI: 10.3762/bjnano.9.55 (Pobrane: 2018-03-20) |
|
|
|
275. |
Rajewsky N., Maier V., Jurga S., Barciszewski J. |
|
|
|
|
|
Systems Biology: Book Series: RNA Technologies Rajewsky N., Jurga S., Barciszewsk J., , V-VII (2018) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-92967-5 (Pobrane: 2020-12-26) |
|
|
|
274. |
Jenczyk J., Woźniak-Budych M., Jarek M., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
European Polymer Journal, 98, 384-393 (2018) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2017.11.045 (Pobrane: 2018-03-20) |
|
|
|
273. |
Baranowska-Korczyc A., Kościnski M., Coy E.L., Grześkowiak B.F., Jasiurkowska-Delaporte M., Peplińska B., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
RSC Advances, 8(43), 24411-24421 (2018) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1039/c8ra02823k (Pobrane: 2020-12-26) |
|
|
|
272. |
Pavlenko M., Siuzdak K., Coy L.E., Jancelewicz M., Jurga S., Iatsunskyi I. |
|
|
|
|
|
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 42(51), 30076-30085 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.10.033 (Pobrane: 2017-12-21) |
|
|
|
271. |
Woźniak-Budych M.J., Przysiecka Ł., Maciejewska B.M., Wieczorek D., Staszak K., Jarek M., Jesionowski T., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 3(12), 3183-3194 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.7b00465 (Pobrane: 2018-03-20) |
|
|
|
270. |
Pogrebnjak A., Ivashchenko V., Bondar O., Beresnev V., Sobol O., Zaleski K., Jurga S., Coy E., Konarski P., Postolnyi B. |
|
|
|
|
|
Materials Characterization, 134, 55-63 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.matchar.2017.10.016 (Pobrane: 2018-03-20) |
|
|
|
269. |
Gołąbiewska A., Lisowski W., Jarek M., Nowaczyk G., Michalska. M., Jurga S., Zaleska-Medyńska A. |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecular Catalysis, 442, 154-163 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.mcat.2017.09.004 (Pobrane: 2018-03-20) |
|
|
|
268. |
Ivashchenko O., Gapiński J., Peplińska B., Przysiecka Ł.,Zalewski T., Nowaczyk G., Jarek M., Marcinkowska-Gapińska A., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Materials & Design, 133, 307-324 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2017.08.001 (Pobrane: 2018-03-20) |
|
|
|
267. |
Woźniak A., Grześkowiak B.F., Babayevska N., Zalewski T., Drobna M., Woźniak-Budych M., Wiweger M., Słomski R., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Materials Science & Engineering C - Materials for Biological Applications, 80, 603-615 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.msec.2017.07.009 (Pobrane: 2018-03-20) |
|
|
|
266. |
Kertmen A., Torruella P., Coy E., Yate L., Nowaczyk G., Gapiński J., Vogt C., Toprak M., Estrade S., Peiro F., Milewski S., Jurga S., Andruszkiewicz R. |
|
|
|
|
|
Langmuir, 33(39), 10351-10365 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b02743 (Pobrane: 2018-03-20) |
|
|
|
265. |
Modrzejewska-Sikorska A., Konował E., Klapiszewski Ł., Nowaczyk G., Jurga S., Jesionowski T., Milczarek G. |
|
|
|
|
|
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 103, 403-408 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.05.083 (Pobrane: 2018-03-19) |
|
|
|
264. |
Stodolny M., Zagrodnik R., Nowaczyk G., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Materials Research Bulletin, 94, 335-341 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2017.06.010 (Pobrane: 2018-03-20) |
|
|
|
263. |
Pogrebnjak A., Rogoz V., Ivashchenko V., Bondar O., Shevchenko V., Jurga S., Coy E. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 718, 260-269 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.05.136 (Pobrane: 2018-03-19) |
|
|
|
262. |
Coy E., Graczyk P., Yate L., Zaleski K., Gapiński J.,Kuświk P., Mielcarek S., Stobiecki F., Mróz B., Ferrater C., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Scientific Reports, 7, 11800 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-12370-y (Pobrane: 2020-10-23) |
|
|
|
261. |
Dobies M., Makrocka-Rydzyk M., Jenczyk J., Jarek M., Spontak R.J., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Langmuir, 33(36), 8856-8868 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b02017 (Pobrane: 2020-10-23) |
|
|
|
260. |
Warowicka A., Maciejewska B.M., Litowczenko J., Kościński M., Baranowska-Korczyc A., Jasiurkowska-Delaporte M., Kozioł K., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Composites Science and Technology, 149, 305-305 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.05.023 (Pobrane: 2018-03-20) |
|
|
|
259. |
Boś-Liedke A. Walawender M., Woźniak A., Flak D., Gapiński J., Jurga S., Kucińska M., Plewiński A., Murias M., Elewa M., Lampp L., Imming P., Tadyszak K. |
|
|
|
|
|
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics, , 1-10 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1007/s12013-017-0824-3 (Pobrane: 2020-10-23) |
|
|
|
258. |
Flak D., Yate L., Nowaczyk G., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Materials Science & Engineering C: Materials for Biological Applications, 78, 1072-1085 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.msec.2017.04.107 (Pobrane: 2018-03-19) |
|
|
|
257. |
Kempiński M., Florczak P., Jurga S., Sliwińska-Bartkowiak M., Kempiński W. |
|
|
|
|
|
Applied Physics Letters, 111(8), 084102 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1063/1.4996914 (Pobrane: 2018-03-19) |
|
|
|
256. |
Mazierski P., Nadolna J., Nowaczyk G., Lisowski W., Winiarski M.J., Klimczuk T., Kobylański M.P., Jurga S., Zaleska-Medyńska A. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 121(32), 17215-17225 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b03895 (Pobrane: 2018-03-19) |
|
|
|
255. |
Iatsunskyi I., Vasylenko A., Viter R., Kempiński M., Nowaczyk G., Jurga S., Bechelany M. |
|
|
|
|
|
Applied Surface Science, 411, 494-501 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.03.111 |
|
|
|
254. |
Kempiński M., Łoś S., Florczak P., Kempiński W., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Acta Physica Polonica A, 132(1), 81-85 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.12693/APhysPolA.132.81 (Pobrane: 2018-03-19) |
|
|
|
253. |
Kempiński M., Jenczyk J., Jurga S., Śliwińska-Bartkowiak M. |
|
|
|
|
|
Acta Physica Polonica A, 132(1), 185-188 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.12693/APhysPolA.132.185 (Pobrane: 2017-11-04) |
|
|
|
252. |
Tadyszak K., Kertmen A., Coy E., Andruszkiewicz R., Milewski S., Kardava I., Scheibe B., Jurga S., Chybczyńska K. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 433, 254-261 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.03.025 |
|
|
|
251. |
Wencka M., Apih T., Korosec R.C., Jenczyk J., Jarek M., Szutkowski K., Jurga S., Dolinsek J. |
|
|
|
|
|
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 19(23), 15368-15376 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1039/c7cp01045a |
|
|
|
250. |
Krysztofik A., Głowiński H., Kuświk P., Ziętek S., Coy L.E., Rychły J.N., Jurga S., Stobiecki T.W., Dubowik J. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 50(23), 235004 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1088/1361-6463/aa6df0 |
|
|
|
249. |
Woźniak A., Malankowska A., Nowaczyk G., Grześkowiak B.F., Tuśnio K., Słomski R., Zaleska-Medyńska A., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Materials Science-Materials in Medicine, 28(6), 92 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1007/s10856-017-5902-y |
|
|
|
248. |
Dobies M., Iżykowska J., Wilkowska M., Woźniak-Braszak A., Szutkowski K., Skrzypczak A., Jurga S., Kozak M. |
|
|
|
|
|
The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 121(21), 11839-11850 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b01801 |
|
|
|
247. |
Jenczyk J., Woźniak-Budych, M., Jarek M., Grzeszkowiak M., Nowaczyk G., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Applied Surface Science, 406, 235-244 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.02.143 |
|
|
|
246. |
Falkowski M., Rębiś T., Piskorz J., Popenda Ł., Jurga S., Mielcarek J., Milczarek G., Gośliński T. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Porphyrins and Phthalocyanines, 21(46) SI, 295-301 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1142/S1088424617500134 (Pobrane: 2018-03-19) |
|
|
|
245. |
Babayevska N., Florczak P., Woźniak-Budych M., Jarek M., Nowaczyk G., Zalewski T., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Applied Surface Science, 404, 129-137 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.01.274 |
|
|
|
244. |
Fantechi E., Roca A.G., Sepulveda B., Torruella P., Estrade S., Peiro F., Coy E., Jurga S., Bastus N.G., Nogues, J., Puntes V. |
|
|
|
|
|
Chemistry of Materials, 29(9), 4022-4035 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b00608 |
|
|
|
243. |
Tillo A., Młynarczyk D.T., Popenda Ł., Wicher B., Kryjewski M., Szczołko W., Jurga S., Mielcarek J., Gdaniec M., Gośliński T., Tykarska E. |
|
|
|
|
|
Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 41(9), 3586-3594 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1039/c6nj03886g (Pobrane: 2021-01-20) |
|
|
|
242. |
Dunst K.J., Scheibe B., Nowaczyk G., Jurga S., Jasiński P. |
|
|
|
|
|
Measurement Science and Technology, 28(5), 054005 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1088/1361-6501/aa57e7 (Pobrane: 2020-10-23) |
|
|
|
241. |
Ivashchenko O., Woźniak A., Coy E., Peplińska B., Gapiński J., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 152, 85-94 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.01.009 (Pobrane: 2021-01-20) |
|
|
|
240. |
Woźniak-Budych M.J., Przysiecka Ł., Langer K., Peplińska B., Jarek M., Wiesner M., Nowaczyk G., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Materials Science. Materials in Medicine, 28(3), 42 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1007/s10856-017-5857-z |
|
|
|
239. |
Falkowski M., Rębiś T., Kryjewski M., Popenda Ł., Lijewski S., Jurga S., Mielcarek J., Milczarek G., Goślińki T. |
|
|
|
|
|
Dyes and Pigments, 138, 190-203 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2016.11.045 |
|
|
|
238. |
Wieczorek E., Piskorz J., Popenda Ł., Jurga S., Mielcarek J., Gośliński T. |
|
|
|
|
|
Tetrahedron Letters, 58(8), 758-761 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2017.01.027 |
|
|
|
237. |
Moliński A., Zaręba J., Iżykowska J., Skupin M., Andrzejewska W., Jurga S., Kozak M. |
|
|
|
|
|
Biophysical Journal, 112(3) S1, 593A (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.11.3191 (Pobrane: 2020-11-05) |
|
|
|
236. |
Skupin M., Iżykowska J., Andrzejewska W., Dobies M., Jurga S., Kozak M. |
|
|
|
|
|
Biophysical Journal, 112(3) S1, 77A (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.11.460 (Pobrane: 2020-11-05) |
|
|
|
235. |
Iżykowska J., Skupin M., Andrzejewska W., Dobies M., Jurga S., Kozak M. |
|
|
|
|
|
Biophysical Journal, 112(3) S1, 156A (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.11.857 (Pobrane: 2020-11-05) |
|
|
|
234. |
Zaręba J., Iżykowska J., Skupin M., Moliński A., Dobies M., Jurga S., Kozak M. |
|
|
|
|
|
Biophysical Journal, 112(3) S1, 156A (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.11.858 (Pobrane: 2020-11-05) |
|
|
|
233. |
Ivashchenko O., Coy E., Peplińska B., Jarek M., Lewandowski M., Zaleski K., Warowicka A., Woźniak A., Babutina T., Jurga-Stopa J., Dolinsek J., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Nanotechnology, 28(5), 055603 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/28/5/055603 |
|
|
|
232. |
Kardava I., Tadyszak K., Gulua N., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Proceedings of SPIE - Eighth International Conference on Graphic and Image Processing (ICGIP 2016), 10225, UNSP 102251Q (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1117/12.2267687 |
|
|
|
231. |
Rajewsky N., Jurga S., Barciszewski J. (Eds.) |
|
|
|
|
|
Diagnostics. Book Series: RNA Technologies, Rajewski N., Jurga S., Barciszewski J. (Eds.),, , V-VII, Springer-Verlag Berlin, Heidelberger Platz 3, d-14197 Berlin, Germany (2017) |
|
|
ISBN: 978-3-319-55520-1 |
|
|
|
230. |
Pyziak M.A., Bartkowiak G., Popenda Ł., Jurga S., Schroeder G. |
|
|
|
|
|
Designed Monomers and Polymers, 20, 144-156 (2017) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1080/15685551.2016.1231048 |
|
|
|
229. |
Coy E. Yate L., Kabacińska Z., Jancelewicz M., Jurga S., Iatsunskyi I. |
|
|
|
|
|
Materials & Design, 111, 584-591 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2016.09.030 (Pobrane: 2018-04-03) |
|
|
|
228. |
Warowicka A., Maciejewska B.M., Litowczenko J., Kościński M., Baranowska-Korczyc A., Jasiurkowska-Delaporte M., Kozioł K., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Composites Science and Technology, 136, 29-38 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2016.09.026 (Pobrane: 2018-03-19) |
|
|
|
227. |
Shypylenko A., Pshyk A.V., Grześkowiak B., Medjanik K., Peplińska B., Oyoshi K., Pogrebnjak A., Jurga S., Coy E. |
|
|
|
|
|
Materials & Design, 110, 821-829 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2016.08.050 (Pobrane: 2018-04-03) |
|
|
|
226. |
Pshyk A.V., Coy L.E., Nowaczyk G., Kęmpiński M., Peplińska B., Pogrebnjak A.D., Beresnev V.M., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Surface & Coatings Technology, 305, 49-61 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2016.07.075 |
|
|
|
225. |
Gołąbiewska A., Malankowska A., Jarek M., Lisowski W., Nowaczyk G., Jurga S., Zaleska-Medyńska A. |
|
|
|
|
|
Applied Catalysis B: Bnvironmental, 196, 27-40 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.05.013 |
|
|
|
224. |
Falkowski M., Rębiś T., Piskorz J., Popenda Ł., Jurga S., Mielcarek J., Milczarek G., Gośliński T. |
|
|
|
|
|
Dyes and Pigments, 134, 569-579 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2016.08.014 |
|
|
|
223. |
Baitimirova M., Viter R., Andzane J., van der Lee A., Voiry D., Iatsunskyi I., Coy E., Mikoliunaite L., Tumenas S., Zaleski K., Balevicius Z., Baleviciute I., Ramanaviciene A., Ramanavicius A., Jurga S., Erts D., Bechelany M. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 120(41), 23716-23725 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b07221 (Pobrane: 2021-01-27) |
|
|
|
222. |
Leszczyński B., Hadjipanayis G.C., El-Gendy A.A., Zaleski K., Śniadecki Z., Musiał A., Jarek M., Jurga S., Skumiel A. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 416, 269-274 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.05.023 (Pobrane: 2018-04-03) |
|
|
|
221. |
Zalas M., Wawrzyńczak A., Półrolniczak P., Sobuś J., Schroeder G., Jurga S., Selli E. |
|
|
|
|
|
PloS ONE, 11(10), e0164670 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164670 (Pobrane: 2018-04-05) |
|
|
|
220. |
Śliwińska M., Garcia-Hernandez C., Kościński M., Dymerski T., Wardencki W., Namieśnik J., Śliwińska-Bartkowiak M., Jurga S., Garcia-Cabezon C., Rodriguez-Mendez M.L. |
|
|
|
|
|
Sensors, 16(10), 1654 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.3390/s16101654 (Pobrane: 2018-04-03) |
|
|
|
219. |
Przysiecka Ł., Michalska M., Nowaczyk G., Peplińska B., Jesionowski T., Schneider R., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 146, 9-18 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.05.041 (Pobrane: 2018-04-03) |
|
|
|
218. |
Majorosova J., Petrenko V.I., Siposova K., Timko M., Tomasovicova N., Garamus V.M., Koralewski M., Avdeev M.V., Leszczyński B., Jurga S., Gazova Z., Hayryan S., Hu C-K, Kopcansky P. |
|
|
|
|
|
Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 146, 794-800 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.07.024 (Pobrane: 2021-01-20) |
|
|
|
217. |
Jenczyk J., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Polymer, 99, 90-96 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2016.07.006 |
|
|
|
216. |
Wołoszczuk S., Jurga S., Banaszak M. |
|
|
|
|
|
Physical Review E, 94(2), 022502 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.94.022502 (Pobrane: 2020-10-23) |
|
|
|
215. |
Woźniak-Budych M.J., Langer K., Peplińska B., Przysiecka Ł., Jarek M., Jarzębski M., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Materials Chemistry and Physics, 179, 242-253 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2016.05.036 (Pobrane: 2020-10-23) |
|
|
|
214. |
Bajerlein D., Adamski Z., Kacalak W., Tandecka K., Wiesner M., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Science of Nature, 103(7-8), 1-17 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1007/s00114-016-1385-9 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
213. |
Pogrebnjak A.D., Bondar O.V., Abadias G., Ivashchenko V., Sobol O.V., Jurga S., Coy E. |
|
|
|
|
|
Ceramics International, 42(10), 11743-11756 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.04.095 (Pobrane: 2018-04-03) |
|
|
|
212. |
Babayevska N., Nowaczyk G., Jarek M., Zaleski K., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 672, 350-355 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.02.189 |
|
|
|
211. |
Reyes Y.C., Coy L.E., Yate L., Jurga S., Gonzalez E.E. |
|
|
|
|
|
ACS Sensors, 1(6), 725-731 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/acssensors.6b00211 |
|
|
|
210. |
Młynarczyk D.T., Lijewski S., Falkowski M., Piskorz J., Szczółko W., Sobotta Ł., Stolarska M., Popenda Ł., Jurga S., Konopka K., Duzgunes N., Mielcarek J., Goślinski T, |
|
|
|
|
|
ChemPlusChem, 81(5), 460-470 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1002/cplu.201600051 |
|
|
|
209. |
Grześkowiak B., Hryhorowicz M., Tuśnio K., Grzeszkowiak M., Zaleski K., Lipiński D., Zeyland J., Mykhaylyk Olga., Słomski R., Jurga S., Woźniak A. |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecular Biotechnology, 58(5), 351-61 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1007/s12033-016-9934-1 |
|
|
|
208. |
Robak E., Coy E., Kotkowiak M., Jurga S., Załęski K., Drozdowski H. |
|
|
|
|
|
Nanotechnology, 27(17), 175706 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/27/17/175706 (Pobrane: 2018-04-03) |
|
|
|
207. |
Michalska M., Florczak A., Dams-Kozłowska H., Gapiński J., Jurga S., Schneider R. |
|
|
|
|
|
Acta Biomaterialia, 35, 293-304 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.02.002 (Pobrane: 2018-04-05) |
|
|
|
206. |
Wieczorek E., Gierszewski M., Popenda Ł., Tykarska E., Gdaniec M., Jurga S., Sikorski M., Mielcarek J., Piskorz J., Gośliński T. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Molecular Structure, 110, 208-214 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2016.01.032 |
|
|
|
205. |
Tillo A., Stolarska M., Kryjewski M., Popenda Ł., Sobotta Ł., Jurga S., Mielcarek J., Gośliński T. |
|
|
|
|
|
Dyes and Pigments, 127, 110-115 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2015.12.017 (Pobrane: 2018-04-03) |
|
|
|
204. |
Gurzęda B., Florczak P., Kempiński M., Peplińska B., Krawczyk P., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Carbon, 100, 540-545 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2016.01.044 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
203. |
Pshyk A.V., Coy E.L., Yate L., Załęski K., Nowaczyk G., Pogrebnjak A.D., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Materials & Design, 94, 230-239 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2015.12.174 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
202. |
Viter R., Iatsunskyi I., Fedorenko V., Tumenas S., Balevicius Z., Ramanayicius A., Balme S., Kempinski M., Nowaczyk G., Jurga S., Bechelany M. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 120(9), 5124-5132 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b12263 (Pobrane: 2018-04-04) |
|
|
|
201. |
Ivashchenko O., Jurga-Stopa J., Coy E., Peplińska B., Pietralik Z., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Applied Surface Science, 364, 400-409 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.12.149 (Pobrane: 2017-12-08) |
|
|
|
200. |
Jenczyk J., Coy E., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
European Polymer Journal, 75, 234-242 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2015.12.020 (Pobrane: 2018-04-04) |
|
|
|
199. |
Tadyszak K., Boś-Liedke A., Jurga J., Baranowski M., Mrówczynski R., Chlewicki W., Jurga S., Czechowski T. |
|
|
|
|
|
Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry, 54(2), 136-142 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1002/mrc.4330 (Pobrane: 2020-10-25) |
|
|
|
198. |
Jurga S., Erdmann V.A., Barciszewski J. |
|
|
|
|
|
Diagnostics. Book Series: RNA Technologies, Erdmann V.A., Jurga S., Barciszewski J. (Eds.), , Springer-Verlag Berlin, Heidelberger Platz 3, d-14197 Berlin, Germany (2016) |
|
|
ISBN: 978-3-319-34175-0 (Pobrane: 2018-04-04) |
|
|
|
197. |
Rogoz V.M., Ivashchenko V.I., Coy E., Kościnski M., Jurga S., Plyushchyk A. |
|
|
|
|
|
International Conference on Nanomaterials: Application & Properties (NAP), UNSP 01NTF11, (2016) |
|
|
(Pobrane: 2018-04-04) |
|
|
|
196. |
Shypylenko A., Pshyk A.V., Medjanik K., Peplińska B., Oyoshid K., Jurga S., Coy E. |
|
|
|
|
|
International Conference on Nanomaterials: Application & Properties (NAP), UNSP 01NTF18, (2016) |
|
|
(Pobrane: 2018-04-04) |
|
|
|
195. |
Mikołajczyk A., Malankowska A.Nowaczyk G., Gajewicz A., Hirano S., Jurga S., Zaleska-Medyńska A., Puzyn T. |
|
|
|
|
|
RSC Advances, 6(92), 89305-89312 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1039/c6en00232c (Pobrane: 2018-04-04) |
|
|
|
194. |
Woźniak A., Noculak A., Gapiński J., Kociołek D., Boś-Liedke A., Zalewski T., Grześkowiak B.F., Kołodziejczak A., Jurga S., Bański M., Misiewicz J., Podhorodecki A. |
|
|
|
|
|
RSC Advances, 6(98), 95633-95643 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1039/c6ra20415e (Pobrane: 2018-04-04) |
|
|
|
193. |
Pavlenko M., Coy E., Jancelewicz M., Karol Załęski K., Smyntyna V., Jurga S.,Iatsunskyi I. |
|
|
|
|
|
RSC Advances, 6(99), 97070-97076 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1039/c6ra21742g (Pobrane: 2018-04-03) |
|
|
|
192. |
Babayevska N., Peplińska B., Jarek M., Yate L., Tadyszak K., Gapiński J., Iatsunskyi I., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
RSC Advances, 6(92), 89305-89312 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1039/c6ra18393j (Pobrane: 2018-04-04) |
|
|
|
191. |
Pajzderska A., Drużbicki K., Kiwilsza A., Gonzalez M.A., Jenczyk J., Jurga S., Mielcarek J., Wąsicki J. |
|
|
|
|
|
RSC Advances, 6(71), 66617-66629 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1039/c6ra07117a (Pobrane: 2018-04-04) |
|
|
|
190. |
Gurzęda B., Florczak P., Wiesner M., Kempiński M., Jurga S., Krawczyk P. |
|
|
|
|
|
RSC Advances, 6(67), 63058-63063 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1039/c6ra10903a (Pobrane: 2018-04-03) |
|
|
|
189. |
Pavlenko M., Myndrul V., Iatsunskyi I., Jurga S., Smyntyna V. |
|
|
|
|
|
Proceedings of SPIE - Nanophotonics VI, 9884, 98842H (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1117/12.2227122
ISBN: 9781510601291 (Pobrane: 2021-01-10) |
|
|
|
188. |
Baranowska-Korczyc A., Jasiurkowska-Delaporte M., Maciejewska B.M., Warowicka A., Coy L.E., Zalewski T., Kozioł K.K., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
RSC Advances, 6(55), 49891-49902 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1039/c6ra09191a (Pobrane: 2018-04-04) |
|
|
|
187. |
Baranowska-Korczyc A., Warowicka A., Jasiurkowska-Delaporte M., Grześkowiak B., Jarek M., Maciejewska B.M., Jurga-Stopa J., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
RSC Advances, 6(24), 19647-19656 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1039/c6ra02486f (Pobrane: 2018-04-03) |
|
|
|
186. |
Mrówczyński R., Jurga-Stopa J., Markiewicz R., Coy L.E., Jurga S., Woźniak A. |
|
|
|
|
|
RSC Advances, 6(7), 5936-5943 (2016) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1039/c5ra24222c |
|
|
|
185. |
Krysiak E., Wypych-Puszkarz A., Krysiak K., Nowaczyk G., Makrocka-Rydzyk M., Jurga S., Ulański J. |
|
|
|
|
|
Synthetic Metals, 209(3), 150-157 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.synthmet.2015.06.028 |
|
|
|
184. |
Maciejewska B.M., Warowicka A., Baranowska-Korczyc A., Zaleski K., Zalewski T., Kozioł K.K., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Carbon, 94, 1012-1020 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2015.07.091 |
|
|
|
183. |
Michalska M., Aboulaich A., Medjahdi G., Mahiou R., Jurga S., Schneider R. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Alloys and Compunds, 645, 184-192 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.04.162 |
|
|
|
182. |
Makrocka-Rydzyk M., Woźniak-Braszak A., Jurga K., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, 71, 67-72 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2015.08.005 |
|
|
|
181. |
Ivashchenko O., Lewandowski M., Peplińska B., Jarek M., Nowaczyk G., Wiesner M., Zaleski K., Babutina T., Warowicka A., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Materials Science & Engineering C - Materials for Biological Applications, 55, 343-359 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.msec.2015.05.023 (Pobrane: 2018-03-29) |
|
|
|
180. |
Lewandowski M., Miłosz Z., Michalak N., Ranecki R., Sveklo I., Kurant Z., Maziewski A., Mielcarek S., Luciński T., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Thin Solid Films, 591(B), 285-288 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2015.04.060 |
|
|
|
179. |
Bartkowiak G., Gawron K., Jurga S., Schroeder G. |
|
|
|
|
|
Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 29(18), 1696-1702 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1002/rcm.7260 (Pobrane: 2018-04-04) |
|
|
|
178. |
Cho H.Y., Krys P, Szcześniak K., Schroeder H., Park S., Jurga S., Buback M., Matyjaszewski K. |
|
|
|
|
|
Macromolecules, 48(18), 6385-6395 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/acs.macromol.5b01592 (Pobrane: 2018-03-29) |
|
|
|
177. |
Iatsunskyi I., Coy E., Viter R., Nowaczyk G., Jancelewicz M., Baleviciute I., Załęski K., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 119(35), 20591-20599 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b06745 |
|
|
|
176. |
Iatsunskyi I., Jancelewicz M., Nowaczyk G., Kempiński M., Peplińska B., Jarek M., Załęski K., Jurga S., Smyntyna V. |
|
|
|
|
|
Thin Solid Films , 589, 303-308 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2015.05.056 |
|
|
|
175. |
Iatsunskyi I., Kempinski M., Nowaczyk G., Jancelewicz M., Pavlenko M., Zaleski K., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Applied Surface Science, 347, 777-783 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.04.172 |
|
|
|
174. |
Choudhury A.R., Sikorska E., van den Boom J., Bayer P., Popenda Ł., Szutkowski K., Jurga S., Bonomi M., Sali A., Zhukov I., Passamonti S., Novic M. |
|
|
|
|
|
PloS ONE, 10(8), e0135455 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135455 (Pobrane: 2020-10-23) |
|
|
|
173. |
Mrówczyński R., Coy L.E., Scheibe B., Czechowski T., Augustyniak-Jabłokow M., Jurga S., Tadyszak K. |
|
|
|
|
|
The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 119(32), 10341-10347 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.5b01524 (Pobrane: 2018-03-29) |
|
|
|
172. |
Sokół B., Woźniak A., Jankowski R., Jurga S., Wąsik N., Shahid H., Grześkowiak B. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Stroke & Cerebrovascular Diseases, 24(8), 1897-1904 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2015.05.002 |
|
|
|
171. |
Matczak M., Schafer R., Urbaniak M., Szymański B., Kuswik P., Jarosz A., Schmidt M., Aleksiejew J., Jurga S., Stobiecki F. |
|
|
|
|
|
Applied Physics Letters, 107(1), 012404 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1063/1.4926357 (Pobrane: 2018-03-29) |
|
|
|
170. |
Gierszewski M., Falkowski M., Sobotta L., Stolarska M., Popenda Ł., Lijewski S., Wicher B., Burdzinski G., Karolczak J., Jurga S., Gdaniec M., Tykarska E., Sikorski M., Mielcarek J., Gośliński T. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A : Chemistry, 307-308, 54-67 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2015.04.003 (Pobrane: 2018-03-29) |
|
|
|
169. |
Gierszewski M., Falkowski M., Sobotta Ł., Stolarska M.,Popenda Ł., Lijewski S., Wicher B., Burdzinski G., Karolczak J., Jurga S., Gdaniec M., Tykarska E., Sikorski M., Mielcarek J., Goślinski T. |
|
|
|
|
|
Cambridge Structural Database, , (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.5517/cc1435n2
DBR: http://dx.doi.org/10.5517/cc1435n2 (Pobrane: 2021-01-07) |
|
|
|
168. |
Rębiś T., Lijewski S., Nowicka J., Popenda Ł., Sobotta Ł., Jurga S., Mielcarek J., Milczarek G., Gośliński T. |
|
|
|
|
|
Electrochimica Acta, 168, 216-224 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2015.03.191 |
|
|
|
167. |
Lewandowski M., Michalak N., Miłosz Z., Ranecki R., Luciński T., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Nanoscience Advances in CBRN Agents Detection, Information and Energy Security, Petkov P., Tsiulyanu D., Kulisch W., Popov C. (Eds.), , 319-324 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1007/978-94-017-9697-2_32
ISBN: 978-94-017-9696-5 (Pobrane: 2021-01-10) |
|
|
|
166. |
Trzaskowska A., Mielcarek S., Lewandowski M., Miłosz Z., Michalak N., Ranecki R., Coy L.E., Jarek M., Luciński T., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Surface and Coating Technology, 271, 13-17 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2015.01.055 (Pobrane: 2018-04-04) |
|
|
|
165. |
Lewandowski M., Scheibe B., Vasileiadis Th., Michalak N., Miłosz Z., Ranecki R., S. Mielcarek S., Luciński T., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Surface and Coating Technology, 271, 87-91 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2015.01.008 (Pobrane: 2018-04-04) |
|
|
|
164. |
Iatsunskyi I., Pavlenko M., Viter R., Jancelewicz M., Nowaczyk G., Baleviciute I., Załęski K., Jurga S., Ramanavicius A., Smyntyna V. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 119(13), 7164-7171 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b01670 |
|
|
|
163. |
Vasylenko A.I., Tokarchuk M.V., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 119(9), 5113-5116 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/jp511532j |
|
|
|
162. |
Woźniak-Braszak A., Jurga K., Nowaczyk G., Dobies M., Szostak M., Jurga J., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
European Polymer Journal, 64, 62-69 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2014.12.039 (Pobrane: 2020-10-23) |
|
|
|
161. |
Iatsunskyi I., Kempiński M., Jancelewicz M., Załęski K., Jurga S., Smyntyna V. |
|
|
|
|
|
Vacuum, 13, 52-58 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2014.12.015 (Pobrane: 2019-10-15) |
|
|
|
160. |
Erdmann V.A., Jurga S., Barciszewski J. |
|
|
|
|
|
Book Series: RNA Technologies, Erdmann V.A., Jurga S., Barciszewski J. (Eds.), , V-VII, Springer-Verlag Berlin, Heidelberger Platz 3, d-14197 Berlin, Germany (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-17305-4
ISBN: 978-3-319-17304-7 (Pobrane: 2018-03-28) |
|
|
|
159. |
Iatsunskyi I., Nowaczyk G., Jurga S., Fedorenko V., Pavlenko M., Smyntyna V. |
|
|
|
|
|
Optik, 126(18), 1650-1655 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2015.05.088 (Pobrane: 2018-03-29) |
|
|
|
158. |
Flak D., Coy E., Nowaczyk G., Yate L., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
RSC Advances, 5(103), 85139-85152 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1039/c5ra17430a (Pobrane: 2018-04-04) |
|
|
|
157. |
Szatkowski T., Wysokowski M., Lota G., Pęziak D., Bazhenov V.V., Nowaczyk G., Walter J., Molodtsov S.L., Stocker H., Himcinschi C., Petrenko L., Stelling A.L., Jurga S., Jesionowski T. Ehrlich H. |
|
|
|
|
|
RSC Advances, 5(96), 79031-79040 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1039/c5ra09379a (Pobrane: 2018-04-04) |
|
|
|
156. |
Bartkowiak G., Popenda Ł., Jurga S., Schroeder G. |
|
|
|
|
|
New Journal of Chemistry, 39(6), 4695-4707 (2015) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1039/c4nj02103g (Pobrane: 2018-04-04) |
|
|
|
155. |
Maciejewska B.M., Coy L.E., Koziol K.K.K., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 118(4), 27861-27869 (2014) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/jp5077142 |
|
|
|
154. |
Szczeszak A., Grzyb T., Śniadecki Z., Andrzejewska N., Lis S., Matczak M., Nowaczyk G., Jurga S., Idzikowski B. |
|
|
|
|
|
Inorganic Chemistry, 53(23), 12243-12252 (2014) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/ic500354t |
|
|
|
153. |
Wencka M., Hahne M., Kocjan A., Vrtnik S., Kozelj P., Korze D., Jaglicic Z., Soric M., Poptevic P., Ivkov J., Smontara A., Gille P., Jurga S., Tomes P., Paschen S., Ormeci A., Armbruster M., Grin Yu., Dolinsek J. |
|
|
|
|
|
Intermetallics, 55, 56-65 (2014) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.intermet.2014.07.007 |
|
|
|
152. |
Pawlak M.A., Jodlowska E., Gierczyk B., Popenda Ł., Jurga S., Kaźmierski R. |
|
|
|
|
|
Multiple Sclerosis Journal, 20(1), P265-186 (2014) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1177/1352458514546077 (Pobrane: 2018-04-04) |
|
|
|
151. |
Kaźmierczak M., Pogorzelec-Glaser K., Hilczer A., Jurga S., Majchrzycki Ł., Nowicki M., Czajka R., Matelski F., Pankiewicz R., Łęska B., Kępiński L., Andrzejewski B. |
|
|
|
|
|
Materiali in Technologije, 48(5), 675-678 (2014) |
|
|
DOI: UDK: 620.3:66.017:621.318 (Pobrane: 2018-03-23) |
|
|
|
150. |
Zhukov I., Choudhury A.R., Sikorska E., Zuperl S., Popenda Ł., Szutkowski K., Novic M., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
The FEBS Journal, 281, 647 (2014) |
|
|
ISSN: 1742-464X (Pobrane: 2018-03-23) |
|
|
|
149. |
Adrjanowicz K., Kamiński K., Dulski M., Jasiurkowska-Delaporte M., Kołodziejczyk K., Jarek M., Bartkowiak G., Hawelek L., Jurga S., Paluch M. |
|
|
|
|
|
Macromolecules, 47(16), 5798-5807 (2014) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/ma5006155 (Pobrane: 2018-03-23) |
|
|
|
148. |
Andrzejewski B., Bednarski W., Kaźmierczak M., Łapiński A., Pogorzelec-Glaser K., Hilczer B., Jurga S., Nowaczyk G., Załęski K., Matczak M., Łęska B., Pankiewicz R., Kępiński L. |
|
|
|
|
|
Composites Part B: Engineering, 64, 147-154 (2014) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2014.04.022 (Pobrane: 2018-04-04) |
|
|
|
147. |
Gierczyk B., Kaźmierczak, M., Popenda Ł., Sporzyński A., Schroeder G., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry, 52(5), 202-213 (2014) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1002/mrc.4051 (Pobrane: 2018-04-04) |
|
|
|
146. |
Iatsunskyi I., Jurga S., Smyntyna V., Pavlenko M., Myndrul V., Zaleska A. |
|
|
|
|
|
Proceedings of SPIE - Optical Micro- and Nanometrology V, 9132, 913217 (2014) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1117/12.2051489
ISBN: 9781628410808 (Pobrane: 2021-01-11) |
|
|
|
145. |
Maciejewska B.M., Jasiurkowska-Delaporte M., Vasylenko A.I., Kozioł K.K., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
RSC Advances, 4(55), 28826-28831 (2014) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1039/c4ra03881a |
|
|
|
144. |
Siuzdak K., Sawczak M., Klein M., Nowaczyk G., Jurga S., Cenian A. |
|
|
|
|
|
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 30(9), 2505-2512 (2014) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1039/c4cp01923g (Pobrane: 2018-03-23) |
|
|
|
143. |
Jenczyk J., Dobies M., Makrocka-Rydzyk M., Wypych A., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
European Polymer Journal, 49(12), 3986-3997 (2013) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2013.09.003 (Pobrane: 2020-10-23) |
|
|
|
142. |
Choudhury A.R., Perdih A., Župerl Š., Sikorska E. Solmajer T., Jurga S., Zhukov I., Novič M. |
|
|
|
|
|
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1828(11), 2609-2619 (2013) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.06.006 |
|
|
|
141. |
Adrjanowicz K., Kaminski K., Wlodarczyk P., Grzybowska K., Tarnacka M., Zakowiecki D., Garbacz G., Paluch M., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecular Pharmaceutics, 10(10), 3934-3945 (2013) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/mp4003915 |
|
|
|
140. |
Strankowska J., Piszczyk L., Strankowski M., Danowska M., Szutkowski K., Jurga S., Kwela J. |
|
|
|
|
|
European Physical Journal - Special Topics, 222(9), 2179-2186 (2013) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1140/epjst/e2013-01994-8 |
|
|
|
139. |
Adrjanowicz K., Kamiński K., Dulski M., Włodarczyk P., Bartkowiak G., Popenda Ł., Jurga S., Kujawski J. Kruk J., K. Bernard M., Paluch M. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Chemical Physics, 139(11), 111103-4 (2013) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1063/1.4820492 (Pobrane: 2020-10-25) |
|
|
|
138. |
Park S., Cho H.Y., Wegner K.B., Burdynska J., Magenau A.J.D., Paik H.J., Jurga S., Matyjaszewski K. |
|
|
|
|
|
Macromolecules, 46(15), 5856-5860 (2013) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/ma401308e |
|
|
|
137. |
Wypych A., Szpotkowski K., Jurga S., Domka L., Kozak M. |
|
|
|
|
|
Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 108, 212-218 (2013) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.03.010 (Pobrane: 2021-01-20) |
|
|
|
136. |
Zhukov I., Lubecka E.A., Popenda Ł., Stodus K., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
The FEBS Journal, 280 S1 SI, 161 (2013) |
|
|
ISSN: 1742-464X (Pobrane: 2018-03-22) |
|
|
|
135. |
Makrocka-Rydzyk M., Wypych A., Dobies M., Jancelewicz M., Jurga S., Cho HY., Gao HF., Matyjaszewski K. |
|
|
|
|
|
Polymer, 54(13), 3341-3349 (2013) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2013.04.004 |
|
|
|
134. |
Cho H.Y., Averick S.E., Paredes E., Wegner K., Averick A., Jurga S., Das S.R., Matyjaszewski K. |
|
|
|
|
|
Biomacromolecules, 14(5), 1262-1267 (2013) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/bm4003199 (Pobrane: 2018-03-22) |
|
|
|
133. |
Rucińska-Sobkowiak R., Nowaczyk G., Krzeszowska M., Ramęda I., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Environmental and Experimental Botany, 87, 100-109 (2013) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2012.09.012 |
|
|
|
132. |
Makrocka-Rydzyk M., Wegner K., Szutkowski K., Kozak M., Jurga S., Gao H. |
|
|
|
|
|
Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 226, 1271-1292 (2012) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1524/zpch.2012.0300 (Pobrane: 2020-10-23) |
|
|
|
131. |
Strankowski M., Strankowska J., Gazda M., Piszczyk L., Nowaczyk G., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Express Polymer Letters, 6(8), 610-619 (2012) |
|
|
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2012.65 |
|
|
|
130. |
Strankowska J., Fojud Z., Jurga S., Strankowski M., White J.L. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Analytical Science & Technology, 2(A), A22-A30 (2011) |
|
|
DOI: 10.5355/JAST.2011.A22
WWW: http://www.jastmag.org/journal/view.php?number=52 |
|
|
|
129. |
Makrocka-Rydzyk M., Wypych A., Szpotkowski K., Kozak M., Jurga S., Gao H.F., Cho H.Y., Matyjaszewski K. |
|
|
|
|
|
Polymer, 52(24), 5513-5520 (2011) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2011.09.020 (Pobrane: 2020-10-23) |
|
|
|
128. |
Jancelewicz M., Fojud Z., Waszkowiak W., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
European Polymer Journal, 47(1), 48-51 (2011) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2010.10.032 |
|
|
|
127. |
Krzaczkowska J., Strankowski M., Jurga S., Jurga K., Pietraszko A. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 356(20-22), 945-951 (2010) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2010.02.005 |
|
|
|
126. |
Jenczyk J., Makrocka-Rydzyk M., Wypych A., Głowinkowski S., Jurga S., Radosz M. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal od Non-Crystalline Solids, 356(11-17), 582-588 (2010) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2009.06.046 (Pobrane: 2020-10-23) |
|
|
|
125. |
Jancelewicz M., Nowaczyk G., Makrocka-Rydzyk M., Wypych A., Fojud Z., Jurga S., Maciejewski H. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 356(11-17), 669-675 (2010) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2009.07.036 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
124. |
Kozak M., Wypych A., Szpotkowski K., Jurga S., Skrzypczak A. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 356(11-17), 747-753 (2010) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2009.07.043 |
|
|
|
123. |
Makrocka-Rydzyk M., Nowaczyk G. , Głowinkowski S., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Polymer, 51(4), 908-912 (2010) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2009.12.027 |
|
|
|
122. |
Szutkowski K., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 114(1), 165-173 (2010) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/jp9072087 |
|
|
|
121. |
Dobies M., Kozak M., Jurga S., Grubb A. |
|
|
|
|
|
Protein and Peptide Letters , 16(12), 1496-1503 (2009) |
|
|
DOI: 10.2174/092986609789839241 |
|
|
|
120. |
Żogał O.J., Fojud Z., Herzig P., Pietraszko A., Lyashchenko A.B., Jurga S., Paderno V.N. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Applied Physics, 106(3), 033514-5 (2009) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1063/1.3190529 |
|
|
|
119. |
Szpotkowski K., Kozak M., Kozak A., Zieliński R., Wieczorek D., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Acta Physica Polonica A , 115(2), 561-564 (2009) |
|
|
DOI: 10.12693/APhysPolA.115.561
WWW: http://przyrbwn.icm.edu.pl/APP/PDF/115/a115z225.pdf (Pobrane: 2021-01-10) |
|
|
|
118. |
Dobies M., Kempka M., Kuśmia S., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Applied Magnetic Resonance, 34(1-2), 71-81 (2008) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1007/s00723-008-0107-7 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
117. |
Nozirov F., Fojud Z., Jancelewicz M., Nazirov A., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Applied Magnetic Resonance, 34(1-2), 193-203 (2008) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1007/s00723-008-0102-z (Pobrane: 2020-10-23) |
|
|
|
116. |
Zalewski T., Lubiatowski P., Jaroszewski J., Szcześniak E., Kuśmia S., Kruczyński J., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Magnetic Resonance Materials in Physics, Biology and Medicine, 21(3), 177-185 (2008) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1007/s10334-008-0108-4 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
115. |
Herzig P., Fojud Z., Żogał O. J., Pietraszko A., Dukhnenko A., Jurga S., Shitsevalova N. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Applied Physics, 103(8), 083534-7 (2008) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1063/1.2903150 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
114. |
Wąsicki J., Fojud Z., Czarnecki P., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Ferroelectrics, 368(1p2), 63-71 (2008) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1080/00150190802367927 (Pobrane: 2020-07-25) |
|
|
|
113. |
Kozak M., Kempka M., Szpotkowski K., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 353(47-51), 4246-4251 (2007) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2007.02.068 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
112. |
Kozak M., Domka L., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Molecular Structure, 846(1-3), 108-111 (2007) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2007.01.038 |
|
|
|
111. |
Szutkowski K., Stilbs P., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 111(43), 15613-15619 (2007) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/jp073696s (Pobrane: 2020-10-23) |
|
|
|
110. |
Orozbaev B., Fojud Z., Makrocka-Rydzyk M., Schroeder G., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics, 208(19-20), 2121-2127 (2007) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1002/macp.200700197 (Pobrane: 2008-01-09) |
|
|
|
109. |
Danch A., Osoba W., Chrobak D., Nowaczyk G., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 90(1), 201-208 (2007) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1007/s10973-006-7599-x |
|
|
|
108. |
Kozak M., Domka L., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 88(2), 395-399 (2007) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1007/s10973-006-8061-9 |
|
|
|
107. |
Jasinska L., Balas A., Haponiuk J.T., Nowaczyk G., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 88(2), 419-423 (2007) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1007/s10973-006-8033-0 |
|
|
|
106. |
Fojud Z., Herzig P., Żogał O. J., Pietraszko A., Dukhnenko A., Jurga S., Shitsevalova N. |
|
|
|
|
|
Physical Review B - Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 75(18), 184102 (2007) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.75.184102 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
105. |
Kozak M., Domka L., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Solid State Phenomena, 130, 257-262 (2007) |
|
|
DOI: 10.4028/3-908451-40-x.257 (Pobrane: 2021-01-10) |
|
|
|
104. |
Wojtyła L., Garnczarska M., Zalewski T., Bednarski W., Ratajczak L., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Plant Physiology, 163(12), 1207-1220 (2006) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.jplph.2006.06.014 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
103. |
Kozak M., Domka L., Foltynowicz Z., Jakubiak P., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Przemysł Chemiczny, 85(8-9), 840-843 (2006) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
102. |
Krzaczkowska J., Szcześniak E., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Molecular Structure, 794(1-3), 168-172 (2006) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2006.02.003 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
101. |
Nozirov F., Nazirov A., Jurga S., Fu R. |
|
|
|
|
|
Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, 29(4), 258-266 (2006) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2005.09.001 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
100. |
Szutkowska L., Peplińska B., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Acta Physica Polonica A, 108(2), 357-370 (2005) |
|
|
DOI: 10.12693/APhysPolA.108.357
WWW: http://przyrbwn.icm.edu.pl/APP/PDF/108/a108z218.pdf (Pobrane: 2021-01-10) |
|
|
|
99. |
Makrocka-Rydzyk M., Orozbaev B., Nowaczyk G., Głowinkowski S., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Acta Physica Polonica A, 108(2), 385 (2005) |
|
|
DOI: 10.12693/APhysPolA.108.385
WWW: http://przyrbwn.icm.edu.pl/APP/PDF/108/a108z221.pdf (Pobrane: 2021-01-10) |
|
|
|
98. |
Dobies M., Kuśmia S., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Acta Physica Polonica A, 108(1), 33 (2005) |
|
|
DOI: 10.12693/APhysPolA.108.33
WWW: http://przyrbwn.icm.edu.pl/APP/PDF/108/a108z104.pdf (Pobrane: 2021-01-10) |
|
|
|
97. |
Krzaczkowska J., Fojud Z., Kozak M., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Acta Physica Polonica A, 108(1), 187-196 (2005) |
|
|
DOI: 10.12693/APhysPolA.108.187
WWW: http://przyrbwn.icm.edu.pl/APP/PDF/108/a108z124.pdf (Pobrane: 2021-01-10) |
|
|
|
96. |
Lubas M., Sitarz M., Fojud Z., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Molecular Structure, 744-747, 615-619 (2005) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2004.12.011 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
95. |
Sitarz M., Handke M., Fojud Z., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Molecular Structure, 744-747, 621-626 (2005) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2004.12.050 (Pobrane: 2020-10-23) |
|
|
|
94. |
Łodziński M., Sitarz M., Stec K., Kozanecki M., Fojud Z., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Molecular Structure, 744-747, 1005-1015 (2005) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2004.12.042 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
93. |
Olek M., Kempa K., Jurga S., Giersig M. |
|
|
|
|
|
2005 NSTI Nanotechnology Conference and Trade Show - NSTI Nanotech 2005, , 167-170 (2005) |
|
|
ISBN: 0976798514 (Pobrane: 2023-03-03) |
|
|
|
92. |
Olek M., Kempa K., Jurga S., Giersig M. |
|
|
|
|
|
Langmuir, 21(7), 3146-3152 (2005) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/la0470784 (Pobrane: 2023-03-03) |
|
|
|
91. |
Kozak M., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Fibres and Textiles in Eastern Europe, 13(5), 93-95 (2005) |
|
|
WWW: http://www.fibtex.lodz.pl/53_22_93.pdf |
|
|
|
90. |
Trejda M., Lazar K., Decyk P., Fojud Z., Jurga S., Ziółek M. |
|
|
|
|
|
Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis A, 158 A, 829-836 (2005) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/s0167-2991(05)80419-7 (Pobrane: 2021-01-02) |
|
|
|
89. |
Wołoszczuk S., Banaszak M., Jurga S., Pakuła T., Radosz M. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Chemical Physics, 121(23), 12044-12049 (2004) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1063/1.1812751 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
88. |
Danch A., Sułkowski W.W, Moczyński M., Radon A., Stelzer F., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 94(3), 1186-1193 (2004) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1002/app.21027 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
87. |
Olek M., Ostrander J., Jurga S., Mohwald H., Kotov N., Kempa K., Giersig M. |
|
|
|
|
|
Nano Letters, 4(10), 1889-1895 (2004) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/nl048950w (Pobrane: 2023-03-03) |
|
|
|
86. |
Wachowicz M., Jurga S., Vilfan M. |
|
|
|
|
|
Physical Review E - Statistical, Nonlinear and Soft Matter Physics, 70, 031701 (2004) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.70.031701 (Pobrane: 2020-10-23) |
|
|
|
85. |
Gnatyuk I., Puchkovska G., Chashechnikova I., Nozirov F., Jurga S., Peplińska B. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Molecular Structure, 700(1-3), 183-189 (2004) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2004.01.048 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
84. |
Kozak M., Foltynowicz Z., Jakubiak P., Fojud Z., Domka L., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Mat. VI Konferencji Naukowo-Technicznej "Polimery i Kompozyty Konstrukcyjne", , 69-74 (2004) |
|
|
(Pobrane: 2021-01-08) |
|
|
|
83. |
Gnatyuk I., Galdyna O., Chashechnikova I., Nozirov F., Jurga S., Peplińska B. |
|
|
|
|
|
Proceedings of SPIE - XVI International Conference on Spectroscopy of Molecules and Crystals, 5507, (2004) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1117/12.569807
ISBN: 9780819454447 (Pobrane: 2021-01-11) |
|
|
|
82. |
Wachowicz M., Wolak_J., Gracz H., Stejskal E.O., Jurga S., McCord E.F., White J.L. |
|
|
|
|
|
Macromolecules, 37(12), 4573-4579 (2004) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/ma049263u (Pobrane: 2020-08-10) |
|
|
|
81. |
Kuroczycki B., Banaszak M., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Computational Methods in Science and Technology, 10(2), 161-167 (2004) |
|
|
DOI: 10.12921_cmst.2004.10.02.161-167
WWW: http://cmst.eu/wp-content/uploads/files/10.12921_cmst.2004.10.02.161-167_Kuroczycki.pdf (Pobrane: 2020-10-23) |
|
|
|
80. |
Wołoszczuk S., Banaszak M., Jurga S., Radosz M. |
|
|
|
|
|
Computational Methods in Science and Technology, 10(2), 219-228 (2004) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1292/cmst.2004.10.02.219-228
WWW: http://cmst.eu/wp-content/uploads/files/10.12921_cmst.2004.10.02.219-228_Woloszczuk.pdf |
|
|
|
79. |
Kozak M., Danch A., Osoba W., Domka L., Stelzer F., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Polymers and Polymer Composites, 12(5), 409-416 (2004) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1177/096739110401200505 (Pobrane: 2021-01-10) |
|
|
|
78. |
Kiersnowski A., Kozak M., Jurga S., Pigłowski J. |
|
|
|
|
|
Polymers and Polymer Composites, 12(8), 727-737 (2004) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1177/096739110401200809 (Pobrane: 2021-01-10) |
|
|
|
77. |
Głowinkowski S., Peplińska B., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, 25(1-3), 1-4 (2004) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2003.03.025 (Pobrane: 2021-01-21) |
|
|
|
76. |
Kuśmia S., Kozak M., Szcześniak E., Domka L., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, 25(1-3), 173-176 (2004) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2003.03.027 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
75. |
Wasyluk L., Peplińska B., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, 25(1-3), 177-184 (2004) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2003.03.028 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
74. |
Dobies M., Kozak M., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, 25(1-3), 188-193 (2004) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2003.03.019 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
73. |
Nowaczyk G., Głowinkowski S., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, 25(1-3), 194-199 (2004) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2003.07.003 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
72. |
Fojud Z., Szcześniak E., Jurga S., Stapf S., Kimmich R. |
|
|
|
|
|
Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, 25(1-3), 200-206 (2004) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2003.07.002 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
71. |
Banaszak M., Wołoszczuk S., Jurga S., Pakuła T. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Chemical Physics, 119(21), 11451-11457 (2003) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1063/1.1622375 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
70. |
Wolak_J., Jia X., Gracz H., Stejskal E.O., White J.L., Wachowicz M., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Macromolecules, 36(13), 4844-4850 (2003) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1021/ma0301449 (Pobrane: 2020-08-10) |
|
|
|
69. |
Fojud Z., Goc R., Kozak A., Jurga S., Wąsicki J. |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecular Physics, 101(10), 1469-1476 (2003) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1080/0026897031000082167 |
|
|
|
68. |
Domka L., Foltynowicz Z., Jurga S., Kozak M. |
|
|
|
|
|
Polymers and Polymer Composites, 11(5), 397-406 (2003) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1177/096739110301100505 (Pobrane: 2021-01-10) |
|
|
|
67. |
Kiersnowski A., Kozak M., Jurga S., Pigłowski J. |
|
|
|
|
|
Prace Naukowe Instytutu Technologii Organicznej i Tworzyw Sztucznych Politechniki Wrocławskiej, 52, 381-384 (2003) |
|
|
(Pobrane: 2020-10-25) |
|
|
|
66. |
Szutkowski K., Klinowski J., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, 22(2-3), 394-408 (2002) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1006/snmr.2002.0087 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
65. |
Banaszak M., Wołoszczuk S., Pakuła T., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Physical Review E - Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, 66(3), 031804 (2002) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.66.031804 |
|
|
|
64. |
Mozgawa W., Fojud Z., Handke A., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Molecular Structure, 614(1-3), 281-287 (2002) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/S0022-2860(02)00262-4 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
63. |
Nozirov F., Szcześniak E., Fojud Z., Dobrzyński P., Klinowski J., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, 22(1), 19-28 (2002) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1006/snmr.2002.0056 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
62. |
Nozirov F., Fojud Z., Klinowski J., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, 21(3-4), 197-203 (2002) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1006/snmr.2002.0060 (Pobrane: 2020-10-23) |
|
|
|
61. |
Kozak M., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Acta Biochimica Polonica, 49(2), 509-513 (2002) |
|
|
DOI: 10.18388/abp.2002_3810
WWW: http://www.actabp.pl/pdf/2_2002/509.pdf (Pobrane: 2021-01-10) |
|
|
|
60. |
Głowinkowski S., Makrocka-Rydzyk M., Wanke S., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
European Polymer Journal, 38(5), 961-969 (2002) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/S0014-3057(01)00272-5 (Pobrane: 2020-10-23) |
|
|
|
59. |
Garbarczyk M., Kuhn W., Klinowski J., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Polymer, 43(11), 3169-3172 (2002) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/S0032-3861(02)00142-8 |
|
|
|
58. |
Głowinkowski S., Kozak M., Nowaczyk G., Domka L., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Facultatis Chemiae Universitatis Studiorum Mickiewiczianae Posnaniensis Annales II, , 73-78 (2002) |
|
|
ISSN: 1644-6364
(Pobrane: 2021-01-13) |
|
|
|
57. |
Domka L., Kozak M., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Facultatis Chemiae Universitatis Studiorum Mickiewiczianae Posnaniensis Annales II, , 65-72 (2002) |
|
|
ISSN: 1644-6364
(Pobrane: 2021-01-13) |
|
|
|
56. |
Wasyluk L., Peplińska B., Klinowski J., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 4(11), 2392-2397 (2002) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1039/b200634k |
|
|
|
55. |
Foltynowicz Z., Jakubiak P., Judek Ł., Kozak M., Kuśmia S., Fojud Z., Domka L., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Mat. V Konferencji Naukowo-Technicznej "Polimery i Kompozyty Konstrukcyjne", , 61-65 (2002) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
54. |
Suchański W., Minkin P., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Molecular Structure, 559(1-3), 179-185 (2001) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/S0022-2860(00)00695-5 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
53. |
Foltynowicz Z., Wienskowski K., Kozak M., Domka L., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Commodity Science in Global Quality Perspectives. Products - Technology, Quality and Envir, , 353-358 (2001) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
52. |
Nozirov F., Kozak M., Domka L., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecular Physics Reports, 33, 102-105 (2001) |
|
|
WWW: http://www.ifmpan.poznan.pl/mol/
ISSN: 1505-1250 (Pobrane: 2021-01-07) |
|
|
|
51. |
Kuśmia S., Szcześniak E., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecular Physics Reports, 33, 184-187 (2001) |
|
|
WWW: http://www.ifmpan.poznan.pl/mol/
ISSN: 1505-1250 (Pobrane: 2021-01-07) |
|
|
|
50. |
Wasyluk L., Peplińska B., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecular Physics Reports, 33, 111-113 (2001) |
|
|
WWW: http://www.ifmpan.poznan.pl/mol/
ISSN: 1502-1250 (Pobrane: 2021-01-07) |
|
|
|
49. |
Szutkowski K., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecular Physics Reports, 33, 179-183 (2001) |
|
|
WWW: http://www.ifmpan.poznan.pl/mol/
ISSN: 1502-1250 (Pobrane: 2021-01-07) |
|
|
|
48. |
Fojud Z., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecular Physics Reports, 33, 172-174 (2001) |
|
|
WWW: http://www.ifmpan.poznan.pl/mol/
ISSN: 1505-1250 (Pobrane: 2021-01-07) |
|
|
|
47. |
Wachowicz M., Fojud Z., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecular Physics Reports, 33, 176-178 (2001) |
|
|
WWW: http://www.ifmpan.poznan.pl/mol/
ISSN: 1505-1250 (Pobrane: 2021-01-07) |
|
|
|
46. |
Garbarczyk M., Kuhn W., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecular Physics Reports, 33, 106-110 (2001) |
|
|
WWW: http://www.ifmpan.poznan.pl/mol/
ISSN: 1505-1250 (Pobrane: 2021-01-07) |
|
|
|
45. |
Suchański W., Jurga S., Pakuła T., Paluch M., Zioło J. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Physics - Condensed Matter, 12(46), 9551-9562 (2000) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1088/0953-8984/12/46/303 |
|
|
|
44. |
Suchański W., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecular Physics Reports, 29, 130-134 (2000) |
|
|
WWW: http://www.ifmpan.poznan.pl/mol/
ISSN: 1505-1250 (Pobrane: 2021-01-07) |
|
|
|
43. |
Czapla Z., Fojud Z., Cieślik J., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecular Physics Reports, 29, 228-231 (2000) |
|
|
WWW: http://www.ifmpan.poznan.pl/mol/
ISSN: 1505-1250 (Pobrane: 2021-01-07) |
|
|
|
42. |
Fojud Z., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecular Physics Reports, 29, 47-50 (2000) |
|
|
WWW: http://www.ifmpan.poznan.pl/mol/
ISSN: 1505-1250 (Pobrane: 2021-01-07) |
|
|
|
41. |
Nozirov F., Fojud Z., Szcześniak E., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Applied Magnetic Resonance, 18(1), 37-45 (2000) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1007/BF03162097 |
|
|
|
40. |
Leszczyński R., Byczkowski B., Jurga S., Korszun S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Applied Magnetic Resonance, 18(1), 147-153 (2000) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1007/BF03162106 |
|
|
|
39. |
Makrocka-Rydzyk M., Głowinkowski S., Jurga S., Meyer W.H. |
|
|
|
|
|
Applied Magnetic Resonance, 18(1), 63-70 (2000) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1007/BF03162099 |
|
|
|
38. |
Fojud Z., Szcześniak E., Jurga K., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Applied Magnetic Resonance, 19(3-4), 413-420 (2000) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1007/BF03162384 |
|
|
|
37. |
Fojud Z., Boeffel C., Szcześniak E., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Molecular Structure, 555, 107-117 (2000) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/S0022-2860(00)00592-5 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
36. |
Kuśmia S., Szcześniak E., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecular Physics Reports, 28, 106-108 (2000) |
|
|
WWW: http://www.ifmpan.poznan.pl/mol/
ISSN: 1505-1250 (Pobrane: 2021-01-07) |
|
|
|
35. |
Peplińska B., Wasyluk L., Łaniecki M., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecular Physics Report, 29, 50-54 (2000) |
|
|
WWW: http://www.ifmpan.poznan.pl/mol/ |
|
|
|
34. |
Suchański W., Szcześniak E., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Physics-Condensed Matter, 11(19), 3907-3914 (1999) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1088/0953-8984/11/19/310 |
|
|
|
33. |
Suchański W., Szcześniak E., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Physics-Condensed Matter, 10(28), 6243-6249 (1998) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1088/0953-8984/10/28/006 |
|
|
|
32. |
Szcześniak E., Głowinkowski S., Suchański W., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, 8(2), 73-79 (1997) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/S0926-2040(96)01292-1 (Pobrane: 2020-10-21) |
|
|
|
31. |
Głowinkowski S., Jurga S., Suchański W., Szcześniak E. |
|
|
|
|
|
Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, 7(4), 313-317 (1997) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/S0926-2040(96)01266-0 (Pobrane: 2020-10-23) |
|
|
|
30. |
Głowinkowski S., Jurga S., Suchański W., Szcześniak E. |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecular Physics Reports, 14, 83-87 (1996) |
|
|
WWW: http://www.ifmpan.poznan.pl/mol/
ISSN: 1505-1250 (Pobrane: 2021-01-07) |
|
|
|
29. |
Makrocka-Rydzyk M., Głowinkowski S., Jurga S., Meyer W.H. |
|
|
|
|
|
Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, 4(6), 353-360 (1995) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/0926-2040(95)00013-G |
|
|
|
28. |
Jurga K., Reynhardt E.C., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Measurement Science and Technology, 5(1), 27-31 (1994) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1088/0957-0233/5/1/005 |
|
|
|
27. |
Jurga K., Reynhardt E.C., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Magnetic Resonance, Series A, 101(1), 74-77 (1993) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1006/jmra.1993.1010 |
|
|
|
26. |
Jurga K., Reynhardt E.C., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Zeitschrift fur Naturforschung Section A-A Journal of Physical Sciences, 48(4), 563-569 (1993) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1515/zna-1993-0405 (Pobrane: 2021-01-10) |
|
|
|
25. |
Fenrych J., Reynhardt E.C., Jurga S., Jurga K. |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecular Physics, 78(5), 1117-1128 (1993) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1080/00268979300100721 |
|
|
|
24. |
Fenrych J., Reynhardt E.C., Jurga S., Jurga K. |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecular Physics, 79(3), 559-569 (1993) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1080/00268979300101451 |
|
|
|
23. |
Szcześniak E., Głowinkowski S., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Proccedings of 15th Conference on Radio and Microwave Spectroscopy, Poznań (Poland), , 89 (1993) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
22. |
Głowinkowski S., Jurga S., Szcześniak E. |
|
|
|
|
|
Zeitschrift fur Naturforschung Section A-A Journal of Physical Sciences, 47(11), 1157-1160 (1992) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1515/zna-1992-1113 (Pobrane: 2021-01-10) |
|
|
|
21. |
Jurga K., Reynhardt E.C., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Magnetic Resonance (1969), 96(2), 302–306 (1992) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/0022-2364(92)90083-J |
|
|
|
20. |
Reynhardt E.C., Jurga S., Jurga K. |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecular Physics, 77(2), 257-278 (1992) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1080/00268979200102431 |
|
|
|
19. |
Reynhardt E.C., Jurga S., Jurga K. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 4(24), 5433-5442 (1992) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1088/0953-8984/4/24/013 |
|
|
|
18. |
Reynhardt E.C., Jurga S., Jurga K. |
|
|
|
|
|
Chemical Physics Letters, 194(4-6), 410-414 (1992) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/0009-2614(92)86074-R |
|
|
|
17. |
Jurga S., Macho V., Hüser B, Spiess H.W. |
|
|
|
|
|
Zeitschrift fur Physik B Condensed Matter, 84(1), 43-49 (1991) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1007/BF01453757 |
|
|
|
16. |
Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Wiadomości Chemiczne, 42(1), 25 (1988) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
15. |
Jurga S., Seliger J., Blinc R., Spiess H.W. |
|
|
|
|
|
Physics Letters A, 116(6), 295-298 (1986) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/0375-9601(86)90598-0 |
|
|
|
14. |
Jurga S., Harbison G.S., Blumich B., Spiess H.W., Fujara F. |
|
|
|
|
|
Berichte der Bunsengesellschaft fur Physikalische Chemie, 90(12), 1153-1159 (1986) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1002/bbpc.19860901207 |
|
|
|
13. |
Jurga S., Spiess H.W. |
|
|
|
|
|
Zeitschrift fur Naturforschung Section A-A Journal of Physical Sciences, 40(6), 602-610 (1985) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1515/zna-1985-0611 (Pobrane: 2021-01-10) |
|
|
|
12. |
Jurga S., Spiess H.W. |
|
|
|
|
|
Berichte der Bunsengesellschaft fur Physikalische Chemie, 89(7), 763-771 (1985) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1002/bbpc.19850890709 |
|
|
|
11. |
Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Physica Status Solidi A, 81(1), 77-85 (1984) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1002/pssa.2210810107 |
|
|
|
10. |
Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Postępy w zastosowaniu technik rezonansowych w chemii, red. Lucjan Sobczyk, PWN Warszawa, , 42-54 (1984) |
|
|
ISBN: 83-01-04687-2 |
|
|
|
9. |
Jurga S., Depireux J. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Magnetic Resonance (1969), 55(1), 12-23 (1983) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/0022-2364(83)90273-1 |
|
|
|
8. |
Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Fizyka w Szkole, 6(167), 330 (1983) |
|
|
ISSN: 0426-3383 (Pobrane: 2021-01-11) |
|
|
|
7. |
Jurga S., Jurga K., Pająk Z. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Magnetic Resonance (1969), 50(2), 175-187 (1982) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1016/0022-2364(82)90047-6 |
|
|
|
6. |
Jurga S., Jurga K., Pająk Z. |
|
|
|
|
|
Journal of Physics C: Solid State Physics, 14(30), 4433-4446 (1981) |
|
|
DOI: 10.1088/0022-3719/14/30/010 (Pobrane: 2020-10-23) |
|
|
|
5. |
Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Postępy Fizyki Molekularnej, 31, 5-22 (1980) |
|
|
(Pobrane: 2021-01-11) |
|
|
|
4. |
Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Wydawnictwo Naukowe Uniwersytetu im. Adama Mickiewicza, 41, (1980) |
|
|
WWW: http://www.press.amu.edu.pl/
ISSN: 0554-825 X |
|
|
|
3. |
Jurga S., Depireux J., Pająk Z. |
|
|
|
|
|
Proccedings of the 18th Ampere Congress on Magnetic Resonance and Related Phenomena, Nottingham (United Kingdom), 11, 403-404 (1975) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
Pająk Z., Jurga K., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Postępy Fizyki, 25(2), 193-197 (1974) |
|
|
WWW: http://www.ptf.net.pl/pl/aktualnosci/informacje-biezace/archiwum-postepow-fizyki/
ISSN: 0032-5430 (Pobrane: 2021-01-11) |
|
|
|
1. |
Pająk Z., Jurga K., Jurga S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Acta Physica Polonica A, A45, 837-842 (1974) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
18. |
NCN OPUS 11 - 2016/21/B/ST8/00477 |
|
|
Nowe, wielozadaniowe nanocząstki w skojarzonej geno- i fototerapii
|
|
|
2017-04-13 - 2021-10-12
|
| | Link: https://projekty.ncn.gov.pl/index.php?projekt_id=330865 |
|
|
|
17. |
NCN OPUS 8 - 2014/15/B/ST4/04946 |
|
|
Kwantyfikacja natlenienia tkanek nowotworowych mierzonych techniką BOLD-MRI-kalibracja oxymetrią EPR
|
|
|
2015-09-22 - 2019-09-21
|
| | Link: https://projekty.ncn.gov.pl/index.php?projekt_id=275857 |
|
|
|
16. |
NCN OPUS 6 - 2013/11/B/ST3/04190 |
|
|
Przestrzenna organizacja nanocząstek za pomocą polimerowych układów samoorganizujących
|
|
|
2014-07-16 - 2017-07-15
|
| | Link: https://projekty.ncn.gov.pl/index.php?projekt_id=241545 |
|
|
|
15. |
PO Kapitał Ludzki, Działanie 4.1 |
|
|
Rozwój kształcenia w zakresie nanotechnologii na Politechnice Poznańskiej w oparciu o współpracę z Centrum NanoBioMedycznym UAM i Universita degli studi di Trieste
|
|
|
2014-04-01 - 2015-06-11
|
|
|
|
14. |
PO Kapitał Ludzki, Działanie 4.3 |
|
|
Rozwój środowiskowych interdyscyplinarnych studiów doktoranckich w zakresie nanotechnologii-elektroniki i fotowoltaiki w Instytucie Fizyki Molekularnej PAN w Poznaniu i na Wydziale Fizyki UAM
|
|
|
2013-01-01 - 2015-12-01
|
|
|
|
13. |
Program Badań Stosowanych (PBS) |
|
|
Nanomateriały o potencjalnym zastosowaniu w biomedycynie
|
|
|
2012-11-01 - 2015-10-01
|
|
|
|
12. |
PO Innowacyjna Gospodarka, Priorytet I Badania i rozwój nowoczesnych technologii, Działanie 1.2 Wzmocnienie potencjału kadrowego nauki |
|
|
Międzynarodowe Projekty Doktoranckie (MPD) The PhD Programme in Nanoscience and Nanotechnology
|
|
|
2010-05-01 - 2015-04-01
|
|
|
|
11. |
N N202 285338 - (PROMOTORSKI) |
|
|
Dynamika molekularna i przejścia fazowe w układach fosfolipidów zmieszanych z surfaktantami
|
|
|
2010-01-01 - 2011-08-31
|
|
|
|
10. |
N N202 285438 |
|
|
Badanie dynamiki molekularnej oraz struktury kopolimerów blokowych metodą NMR oraz spektroskopii dielektrycznej
|
|
|
2010-01-01 - 2011-08-31
|
|
|
|
9. |
PO Kapitał Ludzki, Podziałanie 4.1.1 Wzmocnienie potencjału dydaktycznego uczelni |
|
|
Zintegrowany program wspierający rozwój Uniwersytetu im. Adama Mickiewicza w Poznaniu w zakresie nauk fizycznych: Proinnowacyjne kształcenie, kompetentna kadra, absolwenci przyszłości
|
|
|
2009-07-01 - 2014-11-01
|
|
|
|
8. |
N N202 128536 |
|
|
Badanie wpływu struktury i dynamiki molekularnej w nowych układach polimerowych o strukturze dendrytycznej i gwiazdowej na zdolność do ich samoorganizacji
|
|
|
2009-05-07 - 2012-11-06
|
|
|
|
7. |
PO Infrastruktura i Środowisko, Działanie 13.1 Infrastruktura Szkolnictwa Wyższego |
|
|
Międzyuczelniane Centrum NanoBioMedyczne
|
|
|
2009-04-01 - 2015-02-01
|
|
|
|
6. |
KBN - 3 T09A 05027 2004-2005 |
|
|
Badania wpływu wybranych surfaktantów na strukture modelowych układów fosfolipidowych
|
|
|
2004-11-16 - 2007-11-15
|
|
|
|
5. |
502235-2 |
|
|
Grant SoftComp (6th Framework Programme), Soft Matter Composites - An Approach to Nanoscale Functional Materials
|
|
|
2004-06-01 - 2015-10-30
|
| | Link: http://www.EU-SoftComp.net |
|
|
|
4. |
KBN - 3 T09A 12726 - (PROMOTORSKI) |
|
|
Badanie procesów fizyko-chemicznych w nanoporach za pomocą NMR
|
|
|
2004-05-24 - 2005-05-23
|
|
|
|
3. |
KBN - 2 P03B 14519 - (PROMOTORSKI) |
|
|
Badanie gęstości usieciowania polimerów metodami Magnetycznego Rezonansu Jądrowego
|
|
|
2000-07-16 - 2001-12-31
|
|
|
|
2. |
KBN - 2 P03B 13317 |
|
|
Badania dynamiki molekularnej modelowych układów dwuwarstwowych metodami spektroskopii NMR
|
|
|
1999-09-01 - 2001-12-31
|
|
|
|
1. |
KBN - 2 0149 9101 |
|
|
Badania dynamiki i struktury układów makromolekularnych metodami NMR
|
|
|
1991-10-01 - 1994-09-30
|
|
|
|
24. |
dr Mateusz Olszyna |
|
|
Development and application of fluorescent microsensors for new label-free detection method based on Low-Q Whispering Gallery Modes |
|
|
2024-05-21 |
|
|
Promotor: ✟ prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Promotor: prof. UAM, dr hab. Maciej Wiesner
Promotor pomocniczy: dr. hab. Lars Dähne
|
|
|
|
23. |
dr Klaudia Żebrowska |
|
|
Wielofunkcyjne nanonośniki na bazie polidopaminy do zastosowań biomedycznych |
|
|
2023-05-09 |
|
|
Promotor: ✟ prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Promotor: prof. UAM, dr hab. Luis Emerson Coy Romero
Promotor pomocniczy: dr Bartosz Grześkowiak
|
|
|
|
22. |
dr Zygmunt Miłosz |
|
|
Wytwarzanie i charakteryzacja nanostruktur opartych na epitaksjalnym grafenie |
|
|
2022-09-28 |
|
|
Promotor: ✟ prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Promotor: prof. UAM, dr hab. Mikołaj Lewandowski
|
|
|
|
21. |
dr Beata Wereszczyńska |
|
|
Lipidowe nanocząstki jako potencjalne środki kontrastujące w obrazowaniu MRI |
|
|
2020-07-10 |
|
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Promotor pomocniczy: dr Tomasz Zalewski
|
|
|
|
20. |
dr Oleksandr Pshyk |
|
|
Structural features and tribo-mechanical properties of TiAIBSiN nanocomposite coatings |
|
|
2018-03-16 |
|
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Promotor pomocniczy: prof. dr sci. Aleksandr Pogrebnjak
|
|
|
|
19. |
dr Andrij Vasylenko |
|
|
Nierównowagowa statystyczna teoria i technika ab initio dla modelowych układów elektronowo-jonowych |
|
|
2015-07-10 |
|
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Promotor: prof. Myhailo Tokarchuk
|
|
|
|
18. |
dr Martyna Michalska |
|
|
Novel CuInS2 quantum dots as fluorescent probes for bioimaging: synthesis and characterization |
|
|
2015-06-22 |
|
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Promotor: prof. Raphael Schneider
|
|
|
|
17. |
dr Katarzyna Szcześniak |
|
|
Polimery gwiaździste jako modelowe nanotransportery leków i kwasów nukleinowych: synteza, struktura i dynamika kationowych polimerów gwiaździstych na bazie poli(glikolu etylenowego) |
|
|
2015-03-15 |
|
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Promotor: prof. Krzysztof Matyjaszewski
Opiekun naukowy: dr Monika Makrocka-Rydzyk
|
|
|
|
16. |
dr Barbara Maciejewska |
|
|
Multiwalled carbon nanotube-iron particle hybrids as potential MRI contrast agents: synthesis and characterisation |
|
|
2015-03-02 |
|
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Promotor: dr Krzysztof Kozioł
Opiekun naukowy: dr Barbara Peplińska
|
|
|
|
15. |
dr Bakyt Orozbaev |
|
|
Dynamika molekularna w ligandach makrocyklicznych typu Podand badana za pomocą spektroskopii dielektrycznej i NMR |
|
|
2013-01-18 |
|
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Zbigniew Fojud
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: dr Zbigniew Fojud
|
|
|
|
14. |
dr Kamil Szpotkowski |
|
|
Dynamika molekularna i przejścia fazowe w układach fosfolipidy - surfaktant |
|
|
2012-01-20 |
|
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: dr Marek Kempka, dr Kosma Szutkowski, dr Aleksandra Wypych
|
|
|
|
13. |
dr Jacek Jenczyk |
|
|
Badanie dynamiki molekularnej oraz struktury kopolimerów blokowych metodą NMR oraz spektroskopii dielektrycznej |
|
|
2011-10-21 |
|
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Stanisław Głowinkowski, dr Monika Makrocka-Rydzyk
|
|
|
|
12. |
dr Mariusz Jancelewicz |
|
|
Dynamika molekularna w modyfikowanych polidwumetylosiloksanach badana metodami reologicznymi oraz NMR |
|
|
2008-11-12 |
|
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Zbigniew Fojud, dr Monika Makrocka-Rydzyk
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: dr Zbigniew Fojud
|
|
|
|
11. |
dr Grzegorz Nowaczyk |
|
|
Badanie własności lepkosprężnych hydrożeli metodami reologicznymi oraz NMR |
|
|
2008-07-11 |
|
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Marek Kempka
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: dr Marek Kempka
|
|
|
|
10. |
dr Justyna Krzaczkowska |
|
|
Badanie struktury i dynamiki molekularnej w nanokompozytach typu polimer/glinokrzemian |
|
|
2007-10-12 |
|
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: dr Marek Kempka, dr Zbigniew Fojud
|
|
|
|
9. |
dr Lidia Szutkowska |
|
|
Badanie dynamiki molekularnej w nanoporach za pomocą NMR |
|
|
2007-04-07 |
|
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Barbara Peplińska
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: dr Barbara Peplińska, dr Marek Kempka
|
|
|
|
8. |
dr Maria Dobies |
|
|
Badanie procesów żelowania wodnych roztworów niskometylowanych pektyn za pomocą NMR i reologii |
|
|
2006-01-12 |
|
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: dr Marek Kempka
|
|
|
|
7. |
dr Marcin Wachowicz |
|
|
Badanie lokalnej i kolektywnej dynamiki molekularnej w liotropowych układach ciekłokrystalicznych za pomocą NMR |
|
|
2005-12-09 |
|
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: dr Marek Kempka, dr Zbigniew Fojud
|
|
|
|
6. |
dr Kosma Szutkowski |
|
|
Badanie procesów dyfuzji translacyjnej w liotropowych wodnych roztworach chlorków n-alkiloamoniowych za pomocą NMR |
|
|
2005-06-09 |
|
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: dr Marek Kempka
|
|
|
|
5. |
dr Maciej Garbarczyk |
|
|
Badanie napęczniałych układów makromolekularnych metodami NMR |
|
|
2001-12-14 |
|
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Promotor: prof. Winfried Kuhn
|
|
|
|
4. |
dr Farhod Nozirov |
|
|
Badanie dynamiki molekularnej w polimerach biodegradowalnych za pomocą magnetycznego rezonansu jądrowego |
|
|
2001-11-09 |
|
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Zbigniew Fojud
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: dr Zbigniew Fojud
|
|
|
|
3. |
dr Monika Makrocka-Rydzyk |
|
|
Badanie metodami NMR struktury i dynamiki molekularnej w układach polimerowych na przykładzie polietylenów i jonanów |
|
|
1999-09-30 |
|
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Stanisław Głowinkowski
|
|
|
|
2. |
dr Zbigniew Fojud |
|
|
Badanie za pomocą NMR dynamiki molekularnej w krystalicznym i uwodnionym chlorku dodecyloamoniowym - modelowym układzie błon lipidowych |
|
|
1999-04-09 |
|
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: prof. dr hab. Kazimierz Jurga
|
|
|
|
1. |
dr Paweł Kamasa |
|
|
Opracowanie metody zwiększenia czułości spektrometru MRJ szerokich linii z zastosowaniem cyfrowej detekcji fazowej |
|
|
1996-09-27 |
|
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: inż. Wojciech Porzuckowiak
|
|
|
|
2. |
dr Jagoda Litowczenko-Cybulska |
|
|
Wpływ topografii (nano)materiałów na zachowanie ludzkich komórek neuralnych |
|
|
2020-06-11 |
|
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Anna Goździcka-Józefiak
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Promotor pomocniczy: dr Alicja Warowicka
|
|
|
|
1. |
dr Piotr Minkin |
|
|
Structure and dynamics of bottlebrush macromolecules |
|
|
2011-03-11 |
|
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Tadeusz Pakuła
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Promotor pomocniczy: dr Wiesław Suchański
|
|
|
|
61. |
mgr Lena Śniadała |
|
|
Wytwarzanie i obrazowanie pian stałych z tlenku grafenu metodą elektronowego rezonansu paramagnetycznego |
|
|
2019-12-11 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
|
60. |
mgr Klaudia Golba |
|
|
Matryce z włókien polimerowych w inżynierii tkankowej jako potencjalne opatrunki antybakteryjne |
|
|
2018-05-21 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr inż. Barbara Maciejewska
|
|
|
|
59. |
mgr Adam Klimaszyk |
|
|
Zastosowanie obrazowania jądrowym rezonansem magnetycznym (MRI) in vivo do badania przejścia między hipoksją a nekrozą w guzach nowotworowych |
|
|
2018-05-21 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Tomasz Zalewski
|
|
|
|
58. |
mgr Agata Barańska |
|
|
Badanie procesu relaksacji dielektrycznej bloku poliizoprenowego w dwublokowych kopolimerach poli(styren-b-izopren) o różnej strukturze domenowej |
|
|
2016-07-11 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Maria Dobies
|
|
|
|
57. |
mgr Mateusz Dymecki |
|
|
Dynamika molekularna łączników grup naftalimidowych w bisinterkalatorach:N,N-bis[3-(1,8-naphthalimido)propyl]-N-propylamine i N-ethyl-N,N-bis-[3-(1,8-naphthalimido)propyl]-N-propylammonium iodide, jako potencjalnych leków przeciwnowotworowych, badania metodami spektroskopowymi - FT-IR, Raman, NMR |
|
|
2016-06-30 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr hab. Zbigniew Fojud
|
|
|
|
56. |
mgr Damian Maziukiewicz |
|
|
Kompozyty na bazie polimeru i wielościennych nanorurek węglowych jako potencjalne rusztowania do hodowli komórkowych |
|
|
2016-06-30 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Barbara Maciejewska
|
|
|
|
55. |
mgr Dorota Zomer |
|
|
Badanie segmentalnej i globalnej dynamiki molekularnej poliizoprenu w niesymetrycznym kopolimerze dwublokowym poli(styren-b-izopren) |
|
|
2014-10-23 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Maria Dobies
|
|
|
|
54. |
mgr Beata Wereszczyńska |
|
|
Badanie właściwości nanokompleksu tlenek żelaza/doksorubicyna jako substancji kontrastującej w obrazowaniu metodą magnetycznego rezonansu jądrowego |
|
|
2014-07-09 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Tomasz Zalewski
|
|
|
|
53. |
mgr Magdalena Walawender |
|
|
Poli(tlenek etylenu) 4-ramienny jako modelowy nośnik leków |
|
|
2014-06-13 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Monika Makrocka-Rydzyk
|
|
|
|
52. |
mgr Justyna Iżykowska |
|
|
Badanie segmentalnej i globalnej dynamiki molekularnej poliizoprenu w homopolimerze oraz symetrycznym kopolimerze dwublokowym poli(styren-b-izopren) |
|
|
2013-07-03 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Maria Dobies
|
|
|
|
51. |
mgr Mikołaj Grzeszkowiak |
|
|
Wielościenne nanorurki węglowe w roztworach wodnych |
|
|
2011-08-08 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Maria Dobies
|
|
|
|
50. |
mgr Katarzyna Dreger |
|
|
Dynamika molekularna w kopolimerach blokowych PS-b-PI badana metodą relaksometrii NMR |
|
|
2011-08-02 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Maria Dobies
|
|
|
|
49. |
mgr Katarzyna Szcześniak |
|
|
Dynamika molekularna i separacja fazowa w mieszaninach polidimetakrylanu glikolu etylowego/polibutadienu, badana za pomocą spektroskopii dielektrycznej |
|
|
2011-02-02 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Monika Makrocka-Rydzyk
|
|
|
|
48. |
mgr Paweł Kuczmiński |
|
|
Badanie procesów żelowania niskometylowanych pektyn amidowanych |
|
|
2010-05-25 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Maria Dobies
|
|
|
|
47. |
mgr Szymon Lis |
|
|
Dynamika molekularna modyfikowanych polidwumetylosiloksanów badana za pomocą szerokopasmowej spektroskopii dielektrycznej |
|
|
2010-05-05 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Aleksandra Wypych
|
|
|
|
46. |
mgr Wojciech Kida |
|
|
Wpływ surfaktantów kationowych na dynamikę konformacyjną wodnych roztworów dwustearoilofosfatydylocholiny (DSPC) |
|
|
2007-07-24 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: mgr Kamil Szpotkowski
|
|
|
|
45. |
mgr Marcin Wiliński |
|
|
Badanie przemian fazowych w dwupalmitylofosfatydylocholinie (DPPC) oraz dwustearoilofosfatydylocholinie (DSPC) metodą spektroskopii w podczerwienii |
|
|
2006-09-28 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: mgr Justyna Krzaczkowska
|
|
|
|
44. |
mgr Małgorzata Pawełczyk |
|
|
Produkcja i charakteryzacja nanostruktur |
|
|
2006-08-12 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: prof. dr hab. Michael Giersig
|
|
|
|
43. |
mgr Jacek Jenczyk |
|
|
Badanie dynamiki molekularnej mieszaniny poli(tlenku etylenu) z kwasem laurynowym metodą jądrowego rezonansu magnetycznego |
|
|
2005-07-01 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Stanisław Głowinkowski, dr Monika Makrocka-Rydzyk
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: dr Marek Kempka
|
|
|
|
42. |
mgr Artem Nowicki |
|
|
Zastosowanie obliczeń równoległych w fizyce na przykładzie symulacji dynamiki molekularnej |
|
|
2004-06-30 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Michał Banaszak
|
|
|
|
41. |
mgr Izabela Suchodolska |
|
|
Wpływ stężenia D-glukozy na lepkość i własności reologiczne krwi |
|
|
2004-06-30 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Maria Dobies
|
|
|
|
40. |
mgr Radosław Ostojski |
|
|
Właściwości modelowanej cieczy dwuskładnikowej badane metodą symulacji Monte Carlo |
|
|
2004-06-30 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Michał Banaszak
|
|
|
|
39. |
mgr Maciej Hołoga |
|
|
Badania struktury wodnego roztworu chlorku undecylamoniowego metodą niskokątowego rozpraszania promieniowania rentgenowskiego SAXS |
|
|
2003-06-30 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Maciej Kozak
|
|
|
|
38. |
mgr Maciej Jopek |
|
|
Badanie dynamiki molekularnej kopolimerów biodegradowalnych przy pomocy techniki NMR |
|
|
2003-06-30 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Stanisław Głowinkowski
|
|
|
|
37. |
mgr Sebastian Wołoszczuk |
|
|
Badanie struktury i przejść fazowych stopów kopolimerów dwublokowych metodą symulacji komputerowej |
|
|
2003-06-30 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Michał Banaszak
|
|
|
|
36. |
mgr Marek Borkowski |
|
|
Wizualizacja dwu-ciągłych konfiguracji kopolimerów generowanych w symulacjach Monte-Carlo |
|
|
2003-06-30 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Michał Banaszak
|
|
|
|
35. |
mgr Piotr Łepkowski |
|
|
Relaksacja w krysztale 8CB |
|
|
2002-06-30 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: mgr Bakyt Orozbaev, dr Zbigniew Fojud
|
|
|
|
34. |
mgr Maciej Olek |
|
|
Obrazowanie procesu migracji cieczy do kompozytu polietylenu z mleczanem wapnia |
|
|
2002-06-30 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: mgr Sławomir Kuśmia
|
|
|
|
33. |
mgr Mariusz Błochowiak |
|
|
Badania przejść fazowych chlorku n-octadecylamoniowego metodą oscylacyjnej spektroskopii podczerwieni |
|
|
2001-08-16 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Zbigniew Fojud
|
|
|
|
32. |
mgr Grzegorz Nowaczyk |
|
|
Wykorzystanie spektroskopii 13C NMR w badaniach dynamiki molekularnej polietylenu oraz jego kopolimerów z 1-butenem |
|
|
2001-06-30 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Monika Makrocka-Rydzyk
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: dr Stanisław Głowinkowski
|
|
|
|
31. |
mgr Bartosz Kuroczycki |
|
|
Symulacja komputerowa dwuwymiarowego układu twardych kul |
|
|
2001-06-30 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Michał Banaszak
|
|
|
|
30. |
mgr Mariusz Jancelewicz |
|
|
Badanie dyspersji magnetycznej relaksacji jądrowej spin-siatka w chlorkach n-alkiloamoniowych i ich roztworach wodnych |
|
|
2001-06-30 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: mgr Marcin Wachowicz
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: dr Zbigniew Fojud
|
|
|
|
29. |
mgr Leszek Siwiec |
|
|
Badanie dynamiki molekularnej w kompleksach mocznika i kwasu korkowego za pomocą Magnetycznego Rezonansu Jądrowego |
|
|
2000-09-15 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Zbigniew Fojud
|
|
|
|
28. |
mgr Marcin Wachowicz |
|
|
Badanie tkanki prostaty metodami NMR |
|
|
2000-07-20 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Bogusław Tomiak
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: dr Zbigniew Fojud
|
|
|
|
27. |
mgr Lidia Wasyluk |
|
|
Badanie dynamiki molekularnej chlorku-tert-butylu (CH3)3CCl w objetościach molekularnych MCM-41 metodą 2H NMR |
|
|
1999-07-30 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Barbara Peplińska
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: dr Marek Kempka
|
|
|
|
26. |
mgr Kosma Szutkowski |
|
|
Badanie współczynników dyfuzji translacyjnej w wodnych roztworach chlorku decylamoniowego |
|
|
1999-07-30 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Marek Kempka, dr Barbara Peplińska
|
|
|
|
25. |
mgr Krzysztof Grześkowiak |
|
|
Obrazowanie mózgu myszy metodą tomografii magnetycznego rezonansu jądrowego przy użyciu sekwencjii dyfuzyjnych |
|
|
1999-06-30 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
|
24. |
mgr Piotr Minkin |
|
|
Badanie dynamiki molekularnej 3-faniliny i 2-etyloftalanu za pomocą jądrowego rezonansu magnetycznego 13C |
|
|
1999-04-12 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Wiesław Suchański
|
|
|
|
23. |
mgr Mariusz Rzepecki |
|
|
Badanie dynamiki molekularnej metanolu CD3OD w zeolicie Na-Y metodą 2H NMR |
|
|
1998-09-12 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: mgr Zbigniew Fojud
|
|
|
|
22. |
mgr Maria Dobies |
|
|
Bezinwazyjne obrazowanie owadów metodą mikroskopii MR. Zastosowanie do stadium larwalnego Cossus cossus L.
|
|
|
1998-07-13 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Janusz Hankiewicz
|
|
|
|
21. |
mgr Dariusz Juskowiak |
|
|
Optymalizacja parametrów obrazowania w tomografii magnetycznego rezonansu jądrowego |
|
|
1998-07-12 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: prof. UAM dr hab. Eugeniusz Szcześniak
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: dr Janusz Hankiewicz
|
|
|
|
20. |
mgr Paweł Golon |
|
|
Rezonans magnetyczny w mikroobrazowaniu struktur porowatych |
|
|
1998-07-12 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: prof. UAM dr hab. Eugeniusz Szcześniak
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: dr. Janusz Hankiewicz
|
|
|
|
19. |
mgr Radosław Leszczyński |
|
|
Dwuwymiarowa spektroskopia wymienna magnetycznego rezonansu jądrowego |
|
|
1998-06-30 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Janusz Hankiewicz, mgr Zbigniew Fojud
|
|
|
|
18. |
mgr Maciej Garbarczyk |
|
|
Badanie dynamiki molekularnej benzenu C6D6 w zeolicie typu Na-Y metodą 2H NMR |
|
|
1997-06-30 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Marek Kempka
Wsparcie naukowe: prof. dr hab. Stanisław Kowalak
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: mgr Zbigniew Fojud
|
|
|
|
17. |
mgr Włodzimierz Masierak |
|
|
Dwuwymiarowa spektroskopia magnetycznego rezonansu jądrowego |
|
|
1997-05-10 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: mgr Zbigniew Fojud
|
|
|
|
16. |
mgr Włodzimierz Pijanowski |
|
|
Badanie dynamiki molekularnej dwupentyloftalanu i
dwumetyloftalanu wykonane metodą jądrowego rezonansu magnetycznego 13C.
|
|
|
1996-06-15 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Wiesław Suchański
|
|
|
|
15. |
mgr Michał Woźniak |
|
|
Dynamika molekularna w silikażelach modyfikowanych decylo(dimetylo) silanem badana metodą magnetycznego rezonansu jądrowego |
|
|
1995-12-29 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: mgr Zbigniew Fojud
|
|
|
|
14. |
mgr Barbara Dolska |
|
|
Dynamika molekularna w krystalicznych modelach błon lipidowych na przykładzie chlorku heptadecylalkiloamoniowego C17H35ND3Cl badana metodami MRJ |
|
|
1992-10-02 |
|
Promotor: prof. UAM, dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: mgr Jan Fenrych
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: prof. dr hab. Kazimierz Jurga, dr Jan Jurga
|
|
|
|
13. |
mgr Mirosława Sielicka |
|
|
Dynamika molekularna w krystalicznych modelach błon lipidowych na przykładzie chlorku heptadecylalkiloamoniowego C18H37ND3Cl badana metodami MRJ |
|
|
1992-08-15 |
|
Promotor: prof. UAM, dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: prof. dr hab. Kazimierz Jurga
|
|
|
|
12. |
mgr Zbigniew Fojud |
|
|
Dwuwymiarowa spektroskopia magnetycznego rezonansu jądrowego |
|
|
1992-06-19 |
|
Promotor: prof. UAM, dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: prof. dr hab. Kazimierz Jurga
|
|
|
|
11. |
mgr Renata Piwowarska |
|
|
Badanie dynamiki molekuł wody w solach kwasu nitropruskiego metodą jądrowego rezonansu magnetycznego |
|
|
1991-12-13 |
|
Promotor: prof. UAM, dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
|
10. |
mgr Monika Makrocka |
|
|
Badania dynamiki molekularnej jonanu C19H36N2 (BF4)2 metodą magnetycznego rezonansu jądrowego |
|
|
1991-09-25 |
|
Promotor: prof. UAM, dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: prof. dr hab. Kazimierz Jurga
|
|
|
|
9. |
mgr Piotr Kątowski |
|
|
Dynamika molekularna w silanach modyfikowanych gamma-amino i gamma-chloropropylotriethoxysilanem |
|
|
1991-09-23 |
|
Promotor: prof. UAM, dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: prof. dr hab. Kazimierz Jurga
|
|
|
|
8. |
mgr Ryszard Dolata |
|
|
Dynamika molekularna w silanach modyfikowanych oktadecylo(dimetylo)silanem badana metodami NMR |
|
|
1991-06-30 |
|
Promotor: prof. UAM, dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: prof. dr hab. Kazimierz Jurga
|
|
|
|
7. |
mgr Aneta Woźniak-Braszak |
|
|
Magnetyczny rezonans jądrowy a struktura i dynamika molekularna w krystalicznych modelach błon lipidowych na przykładzie chlorków alkiloamoniowych C9H19ND3Cl i C11H23ND3Cl |
|
|
1990-07-03 |
|
Promotor: dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: prof. dr hab. Kazimierz Jurga
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: prof. dr hab. Kazimierz Jurga
|
|
|
|
6. |
mgr Maciej Frąckowiak |
|
|
Magnetyczny rezonans jądrowy a struktura i dynamika molekularna w krystalicznych modelach błon lipidowych na przykładzie chlorków alkiloamoniowych C10H21ND3Cl i C12H25ND3Cl |
|
|
1990-07-02 |
|
Promotor: dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: prof. dr hab. Kazimierz Jurga
|
|
|
|
5. |
mgr Jan Fenrych |
|
|
Dynamika molekularna, a przejścia fazowe w długołańcuchowych alkiloamonioczterochlorkach cynku (C10H21NH3)2ZnCl4 i (C13H27NH3)2ZnVl4 badana metodami NMR |
|
|
1990-06-30 |
|
Promotor: dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Wsparcie eksperymentalne: prof. dr hab. Kazimierz Jurga
|
|
|
|
4. |
mgr Jan Martinek |
|
|
Wpływ prądu elektrycznego na absorpcję mikrofalową w nadprzewodnikach wysokotemperarturowych |
|
|
1990-05-14 |
|
Promotor: dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Jan Stankowski
|
|
|
|
3. |
mgr Mariusz Popenda |
|
|
Badania strukturalne alkaloidów chinowych metodą jądrowego rezonansu magnetycznego |
|
|
1989-07-28 |
|
Promotor: dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
|
2. |
mgr Aleksander Pecyna |
|
|
Badanie dynamiki molekularnej i stopnia uporządkowania poli-pentyloxytrójfenylenu metodą magnetycznego rezonansu jądrowego |
|
|
1989-05-23 |
|
Promotor: dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
|
1. |
mgr Borysław Czyżak |
|
|
Badania wysokociśnieniowe nadprzewodników wysokotemperaturowych Y-Ba-Cu-O, oraz Tl-Ca-Ba-Cu-O |
|
|
1989-03-07 |
|
Promotor: dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: prof. dr hab. Jan Stankowski
|
|
|
|
6. |
mgr Waldemar Wnuk |
|
|
Badania dynamiki molekularnej w nadchloranach metyloamoniowych metodą MRJ
|
|
|
1982-06-25 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Zdzisław Pająk
Opiekun naukowy: dr Stefan Jurga, dr hab. Kazimierz Jurga
|
|
|
|
5. |
mgr Roman Górny |
|
|
Badania dynamiki molekularnej w nadchloranach metyloamoniowych metodą MRJ
|
|
|
1981-06-25 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Zdzisław Pająk
Opiekun naukowy: dr Stefan Jurga, dr Kazimierz Jurga
|
|
|
|
4. |
mgr Adam Żmudziński |
|
|
Obliczanie energii potencjalnej dla różnych typów reorientacji molekularnych |
|
|
1978-06-30 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Zdzisław Pająk
Opiekun naukowy: dr Stefan Jurga, dr inż Zbigniew Kierzkowski
|
|
|
|
3. |
mgr Anna Szelągowska |
|
|
Badanie dynamiki molekularnej dwupentyloftalanu i
dwumetyloftalanu wykonane metodą jądrowego rezonansu magnetycznego 13C.
|
|
|
1978-06-25 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Zdzisław Pająk
Opiekun naukowy: dr Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
|
2. |
mgr Józef Kubicki |
|
|
Badanie dynamiki molekularnej w nadchloranie trójmetylosulfoniowym metodą impulsową magnetycznego rezonansu jądrowego |
|
|
1977-06-25 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Zdzisław Pająk
Opiekun naukowy: dr Stefan Jurga, dr Kazimierz Jurga
|
|
|
|
1. |
mgr Krzysztof Niemotko |
|
|
Metody pomiaru natężenia pola lokalnego
|
|
|
1976-06-25 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Zdzisław Pająk
Opiekun naukowy: dr Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
|
3. |
lic Radosław Ostojski |
|
|
System wizualizacji molekuł w oparciu o środowisko www |
|
|
2001-06-30 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Michał Banaszak
|
|
|
|
2. |
lic Leszek Banach |
|
|
Symulacje komputerowe metodą dynamiki molekularnej na klastrze komputerów PC |
|
|
2001-06-30 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Michał Banaszak
|
|
|
|
1. |
lic Sebastian Wołoszczuk |
|
|
Symulacje komputerowe kopolimerów trójblokowych z wykorzystaniem algorytmu ruchów kooperatywnych |
|
|
2001-06-30 |
|
Promotor: prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
Opiekun naukowy: dr Michał Banaszak
|
|
|
|
23. |
prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
2012-10-18
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22. |
prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
2012-04-26
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21. |
prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
2012-03-15
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20. |
prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
2011-04-14
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19. |
prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
2011-04-14
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18. |
prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
2011-03-15
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17. |
prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
2010-11-25
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16. |
prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
2010-03-05
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15. |
prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
2009-05-14
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14. |
prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
2008-10-23
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13. |
prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
2008-03-17
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12. |
mgr Mariusz Jancelewicz, dr Marek Kempka, prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
2006-02-24
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11. |
mgr Grzegorz Nowaczyk, prof. Dimitris Vlassopoulos, dr Marek Kempka, prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
2006-02-24
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10. |
prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
2004-01-21
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9. |
prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
2003-05-11
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8. |
prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
1999-10-12
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7. |
prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
1999-05-13
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6. |
prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
1998-11-12
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5. |
prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
1998-03-26
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. |
prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
1997-04-10
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. |
prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
1997-02-06
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
1996-05-23
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. |
prof. dr hab. Stefan Jurga
|
|
|
1996-02-01
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|